Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Plastic film and bag production is rapidly shifting toward eco-friendly practices that balance material performance with environmental responsibility, and this article explains how manufacturers can adopt sustainable technologies such as biodegradable film extrusion, PLA and PBAT processing, and integrated recycling systems. Readers will learn the mechanics behind greener polymers, the energy-saving features that lower carbon footprints, and the equipment classes that enable circular economy outcomes while preserving product quality. Many producers face pressure from regulators, brand customers, and rising raw material costs; this guide offers practical steps to reduce waste, use post-consumer or bio-based feedstocks, and optimize processes for energy efficiency. We will map the benefits of sustainable film manufacturing, compare machine types that support circularity, describe vendor capabilities for biodegradable extrusion, outline trends and regulatory drivers through 2025, and provide operational checklists and case-study frameworks for implementation. Throughout, keywords such as sustainable plastic manufacturing, biodegradable film extrusion, plastic recycling machines, and circular economy plastic are integrated to aid discoverability and to ground technical guidance in real-world manufacturing choices. The following sections dive into benefits, equipment, vendor innovation, regulations, operational tactics, and evidence from field deployments to support actionable decisions.

Sustainable plastic film manufacturing reduces environmental impact, improves operational efficiency, and unlocks market advantages by using biodegradable polymers, recycled feedstock, and energy-optimized equipment. The mechanisms that deliver these benefits include lower lifecycle emissions from bio-based resins, higher material yield from optimized extrusion and winding controls, and reduced landfill pressure when films are compostable or mechanically recycled. These outcomes translate to quantifiable advantages such as lower per-unit energy consumption, reduced scrap rates, and better alignment with brand sustainability commitments that drive premium positioning. Understanding these benefits helps manufacturers prioritize investments in machinery, process controls, and material sourcing that deliver measurable ROI.
Sustainable film manufacturing delivers several core benefits:
These benefits create both immediate and long-term value, and the next paragraph shows how they map to measurable outcomes for planning capital investments.
Different sustainable practices provide distinct, measurable outcomes that help justify equipment or material changes.
| Benefit | Mechanism | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced landfill waste | Use of biodegradable PLA/PBAT or compostable starch blends | Lower end-of-life landfill share; improved product circularity |
| Energy savings | Servo drives, heat recovery, optimized screw profiles | 10–25% energy reduction per ton of film in modern retrofits |
| Material yield increase | Precision die and winding control, inline thickness monitoring | 3–8% less scrap and higher sellable output |
| Regulatory compliance | Adoption of PCR/PIR content and compostable labeling | Faster market access and reduced non-compliance risk |
This table clarifies how specific mechanisms yield concrete performance or compliance benefits and sets the stage for equipment choices that support those mechanisms.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. supplies machinery categories—biodegradable film extrusion machines and plastic recycling machines—that directly support many of the benefits above, and manufacturers evaluating upgrades should consider how machine capability aligns with targeted outcomes. Evaluating extruder designs, die control, and downstream handling for compostable films can reveal the expected reduction in scrap and energy per run, while recycling lines enable closed-loop use of film scrap and PCR resin. For suppliers and inquiries, prospective buyers often request specification matching between production targets and machine classes before trial runs, which helps ensure the chosen equipment delivers the environmental and operational gains described above.
Biodegradable film extrusion uses bio-based or compostable polymers like PLA, PBAT, and starch blends that break down under defined conditions, reducing persistent plastic accumulation and enabling industrial composting or accelerated degradation. These polymers follow distinct degradation pathways—hydrolysis for PLA under heat and moisture, and microbial breakdown for PBAT in composting environments—so material selection and end-of-life infrastructure determine net environmental benefit. Processing requires extrusion systems with precise temperature control, specialized screw profiles, and degassing to prevent thermal degradation and preserve mechanical properties, which helps maintain film clarity and sealability. When manufacturers pair proper processing with clear labeling and compatible downstream waste management, biodegradable extrusion can materially reduce long-term environmental risk while meeting functional packaging requirements.
Processing considerations drive material performance and determine compostability outcomes, and the next section discusses how energy efficiency further reduces lifecycle impacts.
Energy efficiency in film production reduces greenhouse gas emissions and operating costs by improving per-unit energy consumption through equipment and process improvements such as high-efficiency motors, servo-driven systems, and optimized thermoregulation. At the machine level, equipping extruders and winding units with variable-frequency drives, energy-recovering heaters, and insulated barrels reduces idle losses and peak demand, while process-level measures—balanced throughput versus melt temperature and coherent line speeds—minimize rework and associated energy waste. Factory-level strategies like heat recovery from cooling systems and centralized energy management platforms enable measured reductions in carbon footprint and predictable operating cost declines. Demonstrable savings vary by facility but retrospective analyses often show double-digit percentage reductions in energy per ton after combined machine and process upgrades.
Implementing energy efficiency creates operational resilience and positions manufacturers to meet evolving carbon targets, which leads naturally into the types of equipment that enable circular economy goals.
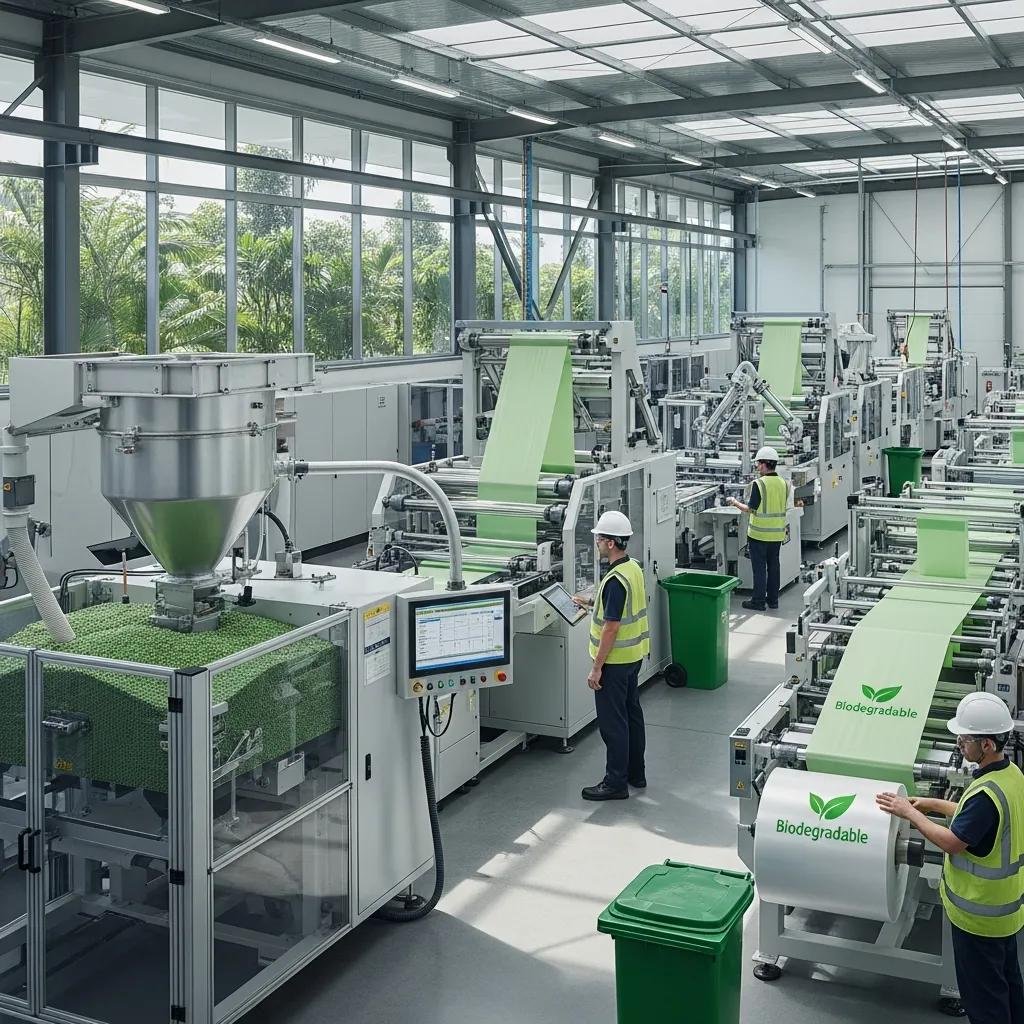
Eco-friendly bag production relies on three machine categories—biodegradable bag making machines, blown film extrusion lines capable of PLA/PBAT processing, and plastic recycling machines that reclaim scrap and PCR feedstock—to close material loops and lower virgin resin use. Each machine class plays a distinct role: blown film extruders form films from bio-based or recycled resin, bag making machines convert films into finished bags with low thermal stress for compostable materials, and recycling pelletizers process film scrap and post-consumer inputs into reusable pellets. Selecting compatible combinations allows manufacturers to produce compostable products while simultaneously integrating recycling for non-compostable streams, thereby supporting circular economy outcomes.
These machine classes combine to form a production ecosystem, and the table below compares typical capabilities for buyer reference.
| Machine Type | Material Compatibility / Energy Consumption | Output Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradable bag making machines | PLA, PBAT, starch blends / ~10–15 kW | 100–300 pcs/min (depending on size) |
| Blown film extrusion machines | PLA, PBAT, PCR blends / ~15–30 kW | 100–600 kg/h (line dependent) |
| Recycling pelletizers / washing lines | PCR/PIR films / ~8–20 kW | 50–400 kg/h reclaimed pellets |
This comparison helps buyers align machine selection with production and sustainability targets and transitions into process-level adjustments needed for polymer-specific handling.
When processing PLA and PBAT, equipment must minimize thermal history and use appropriate cooling and winding strategies to preserve compostability; Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. offers biodegradable bag making machines and lines that handle PLA/PBAT blends and provide configuration options for low-heat sealing and careful web handling. Brief vendor consultation typically focuses on matching material characteristics to die design, heating zones, and downstream handling to prevent polymer degradation while meeting throughput expectations.
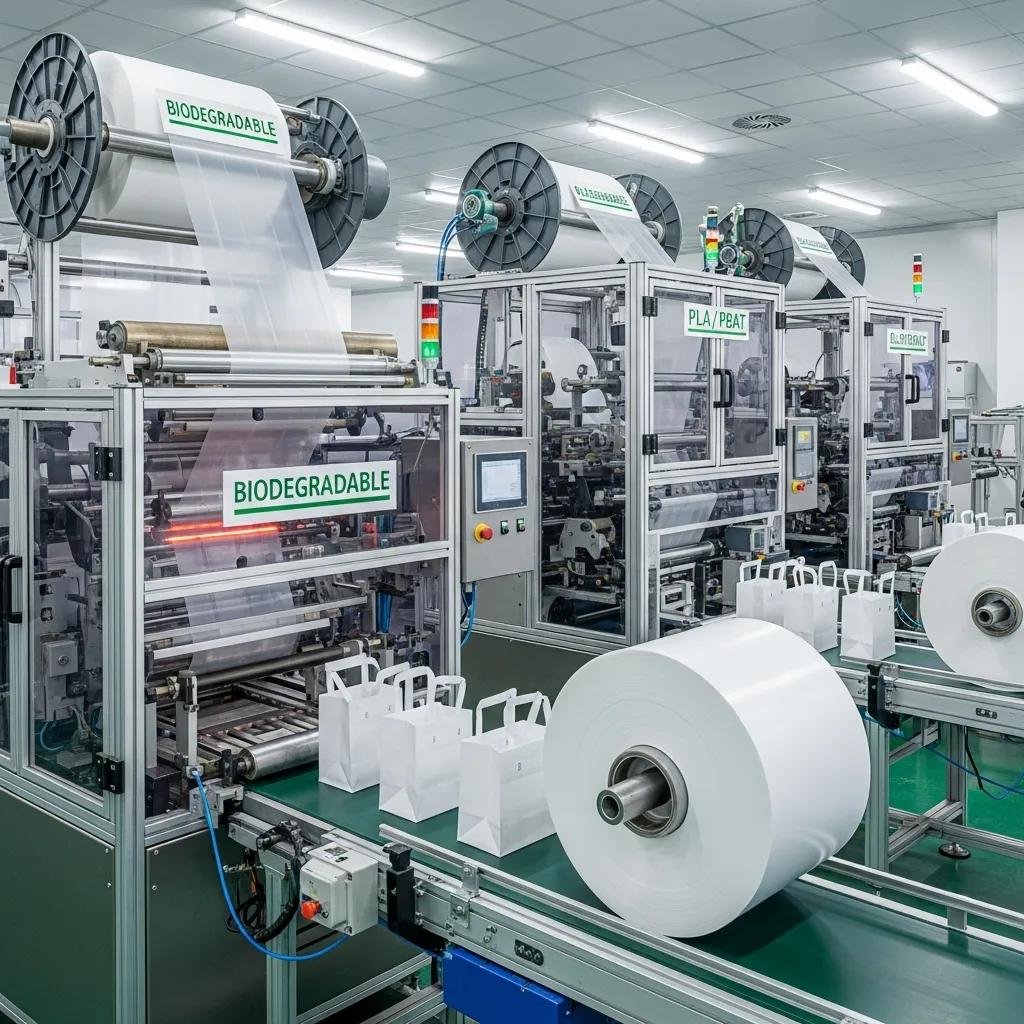

Biodegradable bag making machines are configured to handle PLA and PBAT by controlling thermal profiles, using low-temperature sealing elements, and adjusting winding tension to prevent film stretching that compromises compostable properties. Feedstock preparation emphasizes uniform pellet drying and consistent melt flow; extruder screws and die heads designed for low-shear processing reduce polymer chain scission and preserve mechanical integrity. Additives or compatibilizers may be blended cautiously to improve seal strength or flexibility without undermining compostability standards, and inline quality checks—thickness, seal strength, and compostability testing—ensure finished bags meet performance and end-of-life expectations. Proper machine setup and ongoing monitoring are essential to produce consistent, certifiable compostable bags at industrial throughput.
Careful material handling prevents performance failures during downstream conversion, and the next subsection explains how recycling equipment complements these operations.
Plastic recycling machines—washing lines, granulators, and pelletizers—enable producers to reclaim post-industrial scrap and compatible post-consumer film into reprocessable pellets, reducing virgin resin purchases and diverting waste from landfill. These systems improve circularity by converting process offcuts and collected PCR into consistent feedstock when equipped with robust washing, density separation, and moisture removal before pelletizing. Reclaimed pellets typically require blending strategies and quality control to maintain film properties, but when integrated properly they lower material costs and embodied carbon per unit while reinforcing sustainability claims. Recycling output quality influences permissible PCR ratios in final films, and process controls must balance reclaimed content with functional performance goals.
Integrating recycling workflows requires careful planning around material sorting and quality assurance, which leads into vendor capabilities that support both extrusion and recycling integration.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also identified as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) positions itself as a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and bag production equipment with an eco-focused product range that includes biodegradable bag making machines and plastic recycling machines. The company highlights strong R&D capabilities across product, structural, software, and circuit engineering that inform machine design for biodegradable polymer processing. Reported value propositions include a 100% final inspection policy, a two-year warranty on timer switches, one-stop custom services (logo, label, packaging), competitive pricing through large-scale production and trained staff, and fast delivery timelines—samples within three days and bulk shipments within 15–20 days. Kingdom Machine also emphasizes environmental responsibility by designing machines to minimize energy consumption and offering recycling machines to support circular manufacturing.
These vendor strengths make it easier for manufacturers to evaluate turnkey or modular upgrades, and the next paragraph outlines specific machine features that embody these claims.
Key features attributed to Kingdom Machine’s biodegradable film extrusion equipment include specialized screw geometries tailored for low-shear melt, precise multi-zone temperature control to avoid polymer degradation, and degassing units that improve film clarity and consistency for compostable blends. Downstream systems emphasize gentle cooling, adjustable winders, and low-temperature sealing provisions to preserve biodegradability while meeting production speeds. The company’s quality assurance practices—100% final inspection—and component warranties on critical parts like timer switches are designed to reduce downtime and protect process reliability for sensitive materials. Customization options for die heads, coatings, and packaging integration help manufacturers adopt production setups optimized for their chosen bio-based or recycled feedstocks.
Feature-driven design reduces scrap and energy consumption, and the next subsection explains how customization amplifies those sustainability benefits.
Customization—ranging from tailored die geometry to specialized winding and integrated printing—lets manufacturers optimize machines for specific sustainable materials and production goals, improving yield and reducing waste. For example, retrofitting tension-control winding and low-temperature sealing enables higher PCR or compostable film throughput without tearing or delamination, while bespoke die designs can produce thinner films that meet strength targets with less material. Customization also supports packaging and labeling requirements needed for compostability claims or recycled-content declarations, helping brands communicate sustainability credentials. Collaboration on customization typically shortens time-to-product maturity and supports pilot testing to validate performance before scaling.
Industry trends through 2025 emphasize rising demand for compostable packaging, mandates for increased post-consumer recycled content, and technological investment in recycling and chemical-recycling R&D to handle mixed waste streams. Material science advances—improved PLA/PBAT blends, compatibilizers for PCR, and nanocomposite reinforcement—are expanding functionality while maintaining sustainability credentials. Regional regulations increasingly require recycled content quotas, labeling transparency, and restrictions on certain single-use plastics, prompting manufacturers to upgrade equipment and supply chains. These regulatory and market signals accelerate capital allocation toward extrusion lines that accept PCR, recycling systems, and energy-efficient upgrades that help meet emissions and compliance targets.
The following table maps representative regulatory drivers to practical implications for manufacturers.
| Region / Regulation | Requirement | Implication for Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|
| Mandatory PCR quotas | Minimum recycled content percentages in packaging | Invest in recycling lines and blend controls to meet targets |
| Compostability standards | Certification and labeling for industrial composting | Use compatible polymers and validate end-of-life testing |
| Single-use plastic bans | Restrictions on specified items | Shift to compostable alternatives or reusable models |
Understanding these drivers helps manufacturers prioritize equipment and process changes, and the next paragraphs cover how regulations translate into operational decisions.
Global environmental regulations are compelling manufacturers to redesign packaging with specified recycled content levels, clearer end-of-life labeling, and limits on non-recyclable single-use items; complying requires both material reformulation and equipment adjustments. Practical actions include validating PCR supply chains, investing in washing and pelletizing capacity, and adopting standard testing protocols for compostability or recyclability to substantiate claims. Regulations also create market opportunities for certified sustainable packaging and incentivize partnerships with waste-management providers to ensure proper end-of-life handling. Manufacturers that proactively align machines, materials, and testing can reduce compliance risk and capitalize on evolving buyer preferences.
These regulatory changes shape capital spending decisions and market positioning, and the next subsection assesses market growth dynamics that inform investment timing.
Market forecasts show growing demand for biodegradable films and recycling equipment driven by retail brand commitments and consumer preference for sustainable packaging, with projected compound annual growth rates (CAGR) in specialized segments ranging from 8% to 12% through 2025. Geographic leaders vary: some regions adopt PCR mandates and compostability standards faster, while others scale recycling infrastructure more slowly, which affects where to deploy certain technologies first. Investment patterns indicate increasing interest in lines that can handle blended feedstocks and modular recycling integration to hedge against material supply variability. R&D directions such as chemical recycling and improved compatibilizers aim to expand usable PCR volumes in high-performance films, influencing machine specifications for future-proofing capital equipment.
Anticipating these trends helps manufacturers choose equipment architectures that balance near-term compliance with long-term adaptability, leading into practical implementation advice.
Manufacturers can implement energy-efficient and waste-reducing practices through a mix of machine upgrades, process optimization, and on-site recycling that together reduce per-unit energy use and material loss. Key actions include retrofitting servo drives and high-efficiency motors, deploying inline thickness and tension control to cut scrap, and installing recycling pelletizers to reclaim offcuts and post-industrial scrap. Monitoring systems that track energy usage per run and scrap rates enable continuous improvement and rapid corrective action. These measures produce measurable savings and lower the carbon footprint of film and bag production when combined with targeted material choices.
A practical checklist of actions to implement energy and waste reductions follows and is suitable for operational planning and PAA-style answers.
Applying this checklist yields operational improvements, and the following paragraph discusses specific production practices that minimize carbon footprint.
Sustainable production practices that minimize carbon footprint combine material choices, energy management, and process discipline: sourcing PCR or bio-based resins reduces embodied carbon; installing energy management systems and heat recovery curbs operational emissions; and optimizing run rates and changeovers reduces scrap-related waste. Quick wins include switching to high-efficiency motor drives and implementing automated shutoffs for idle equipment, while longer-term investments might include integrated recycling lines and advanced extrusion designs for thinner, stronger films. Supplier verification and life-cycle assessments guide material selection to ensure claimed carbon reductions are real, not just shifted downstream. These coordinated practices deliver quantifiable carbon and cost benefits over time.
Reducing carbon footprint is tightly coupled with recycling strategies, which are detailed next.
Plastic recycling machines enable on-site reclamation of production scrap and preparation of post-consumer films for reprocessing by executing sorting, washing, granulating, and pelletizing steps that restore material to extrusion-grade form. Quality control—moisture removal, contaminant screening, and melt-index testing—determines acceptable blending ratios for finished films, and incremental increases in PCR usage lower virgin resin demand and embodied emissions per product. Economic trade-offs exist; recycling investments pay off when scrap volumes and PCR demand are sufficient to justify capital cost, but even modest pelletizing capacity can significantly reduce disposal costs and material procurement volatility. Integrating recycling into production planning reduces resource consumption and supports circular product claims in the marketplace.
Having outlined practices and equipment, the final sections point to case studies and client outcomes that demonstrate real-world benefits.
Case studies of eco-friendly film and bag production illustrate practical applications of biodegradable polymers, recycling integration, and energy optimization; summaries help manufacturers evaluate comparable use cases and expected results. Real-world examples typically follow a template—challenge → solution (machine + material) → outcome with metrics—and provide insights into implementation timelines, customization needs, and measurable benefits. Access to full case studies or pilot trials helps buyers validate supplier claims and assess compatibility with their product specifications. These narratives also highlight how coordination between material suppliers, machine makers, and waste management partners ensures successful circularity outcomes.
Example 1 — A mid-sized packager needed compostable produce bags and faced frequent film breakage using conventional settings. The solution used a PLA/PBAT-optimized blown film line with low-shear screws, degassing, and a low-temperature bag maker; result: stable runs at target throughput with a 5% reduction in scrap and verified industrial compostability.
Example 2 — A manufacturer with high offcut volume installed inline pelletizing and washing; solution: reclaiming post-industrial scrap into blended PCR pellets used at 20% in secondary film grades; result: 12% lower virgin resin purchases and a shorter payback on recycling equipment.
Example 3 — A brand shifting to higher PCR content deployed automated thickness control and optimized winding to maintain product strength at 15% PCR, enabling market claims without loss of performance.
Clients working with Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. report benefits that align with the company’s stated value propositions: improved operational reliability supported by 100% final inspection, reduced downtime through warranty-backed components such as timer switches, and accelerated pilot-to-production timelines thanks to rapid sample delivery. Customization services—logo, label, packaging integration—help brands meet sustainability communication requirements while retaining production efficiency. Competitive pricing and trained production staff reportedly shorten lead times for bulk orders, while recycling machine options enable closed-loop material strategies that directly lower virgin resin use and disposal costs. These service and product attributes support tangible sustainability and business outcomes for manufacturers prioritizing eco-friendly production.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;
film blown machine, blown film extrusion, plastic bag making machine
At Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., we specialize in providing high-quality machinery tailored for the plastic bag and blown film manufacturing industries. Our commitment to excellence ensures that our clients receive reliable and efficient equipment that meets their specific production needs.
With years of experience in the industry, we understand the challenges faced by manufacturers. That's why we offer a range of machines designed to enhance productivity while maintaining top-notch quality. From automatic T-shirt bag making machines to advanced blown film machines, our products are engineered to deliver superior performance and durability.
Our commitment to innovation sets us apart in the plastic machinery industry. We continuously invest in research and development to integrate the latest technology into our machines, ensuring they operate at peak efficiency and produce high-quality products.
For instance, our advanced film blowing machines utilize cutting-edge technology to optimize the extrusion process, resulting in consistent film thickness and excellent tensile strength. This not only enhances the quality of the finished product but also reduces material waste, making our machines an eco-friendly choice for manufacturers.
At Kingdom Machinery, we prioritize our customers' needs and satisfaction. Our dedicated support team is available to assist clients throughout the entire process, from selecting the right machinery to providing after-sales service and maintenance.
We believe that strong customer relationships are built on trust and reliability. That's why we offer flexible customization options for our machines, ensuring they fit seamlessly into our clients' production lines. Our timely after-sales service further reinforces our commitment to providing exceptional support.
As a leading manufacturer of plastic bag machinery, we recognize the importance of environmental sustainability. Our machines are designed to minimize energy consumption and reduce waste, aligning with global efforts to promote eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
We also offer a range of recycling machines that facilitate the processing of plastic waste into reusable materials, helping businesses contribute to a circular economy. By choosing our machinery, clients not only improve their production efficiency but also play a vital role in protecting the environment.