Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.
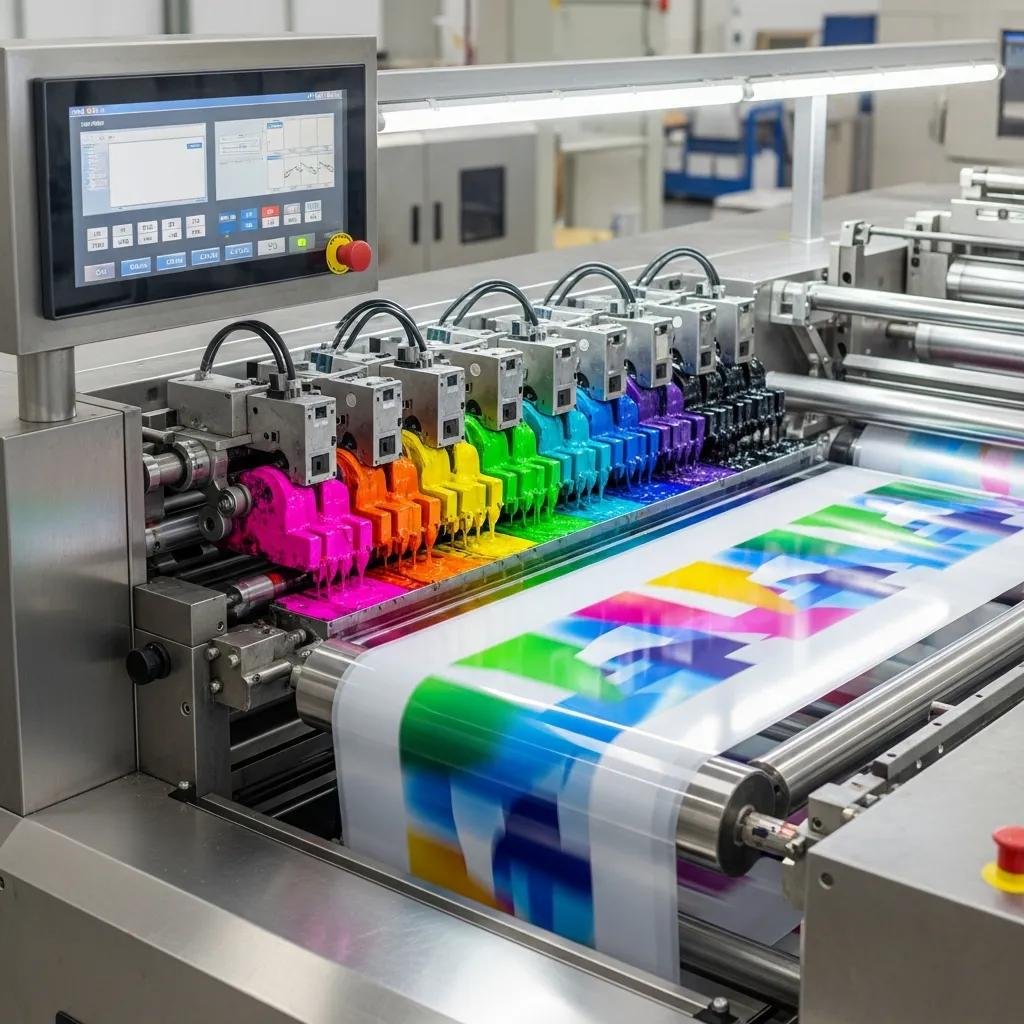

Plastic-film printing inks are the engineered coatings that translate design into durable, functional packaging on substrates like PE, PP, PET, BOPP, and nylon. This guide explains why choosing the right flexo or gravure ink chemistry matters: ink formulation dictates adhesion, drying or curing strategy, color strength, and regulatory compliance, all of which determine print quality and production efficiency. Readers will learn to differentiate water-based, solvent-based, and UV-curable options for both flexography and gravure, assess substrate compatibility and drying systems, and apply practical checks for food-contact and VOC-sensitive applications. The article maps common failure modes—poor wetting, ink migration, slow cure—and matches them to mechanical and chemical solutions such as corona treatment, proper viscosity control, and integrated drying or UV-cure units. Finally, we show how press features influence ink choice and describe machine capabilities that help optimize ink performance while pointing to equipment suppliers that can support ink workflows.
This introduction sets the stage for five technical sections: main flexo ink types and their operational implications; gravure ink families and high-resolution requirements; a decision framework for ink selection focused on substrate, drying, durability, and regulation; how Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd.’s flexo and gravure equipment can support ink performance and maintenance; and environmental plus food-safety considerations that shape modern ink choices. Throughout, target keywords such as flexo inks, gravure inks, plastic film ink compatibility, and UV-curable gravure inks are integrated in context to aid practical selection and implementation.
The next section begins by defining the principal flexo ink chemistries used on plastic films and how their mechanisms influence production outcomes.
Flexo inks for plastic films fall into three main chemistries—water-based, solvent-based, and UV-curable—each defined by its carrier, drying/curing mechanism, and adhesion profile. Water-based flexo inks use water as the primary carrier and rely on evaporative and film-forming mechanisms, offering low VOCs and regulatory advantages but requiring higher substrate surface energy or pretreatment. Solvent-based flexo inks evaporate organic solvents to form a durable film and typically adhere better to non-porous substrates at high press speeds, but they bring VOC management needs. UV-curable flexo inks polymerize under UV energy to instantly fix high-gloss, durable films that enable high throughput with minimal solvent emissions, though they require integrated UV cure systems and attention to ink-film thickness and substrate heat sensitivity.
Below is a compact comparison to help choose between flexo ink families based on typical production priorities.
| Ink Family | Drying/Curing | Typical Substrates | Key Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water-based flexo | Evaporation/film formation | Treated PE/PP, PET with corona | Low VOC, needs good surface energy and robust drying |
| Solvent-based flexo | Solvent evaporation | Metallized films, untreated polyolefins | Strong adhesion, fast dry, higher VOC and safety needs |
| UV-curable flexo | Photopolymerization | PE/PP/PET with UV-stable topography | Instant cure, high gloss, needs UV units and correct ink formulation |
This table highlights how the carrier and cure method predict compatibility and trade-offs, guiding the next step: examining water-based flexo performance in more detail.
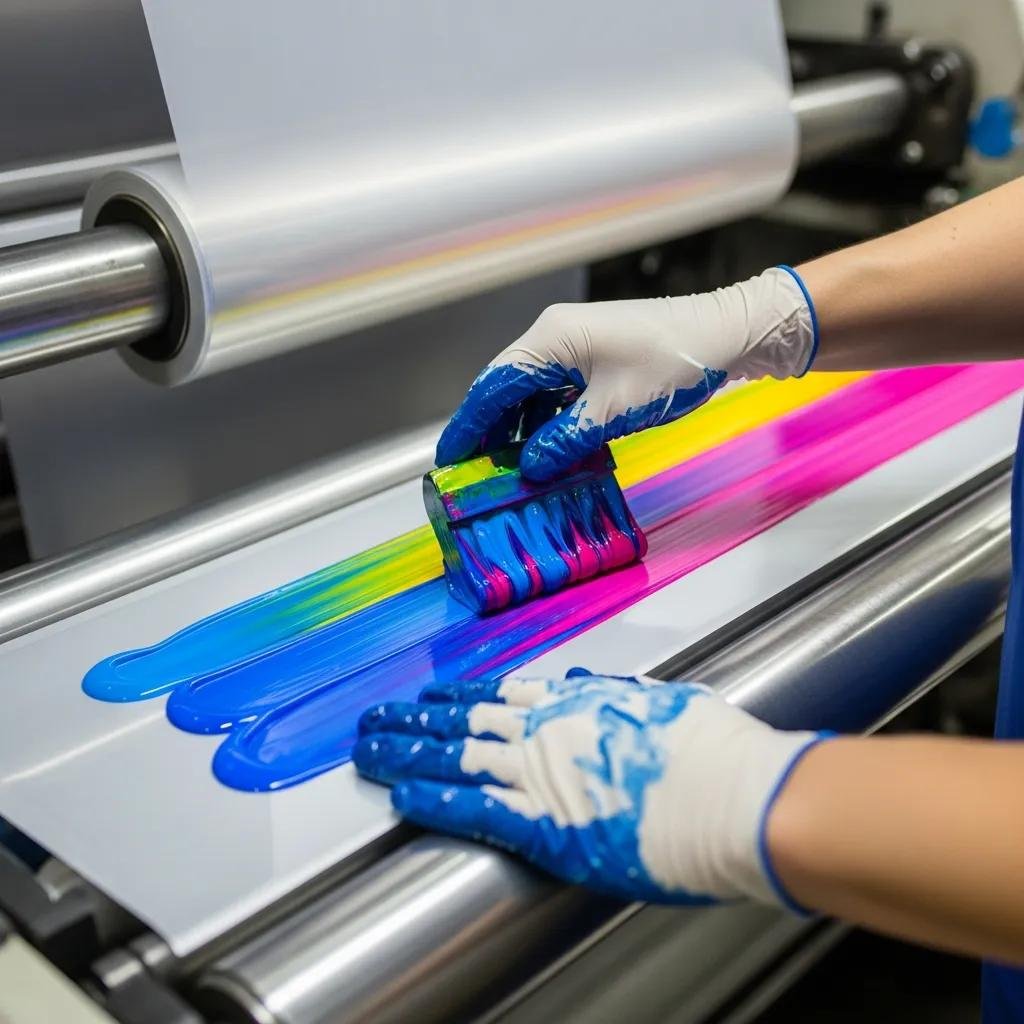

Water-based flexo inks deliver environmental advantages and low VOC emissions because water is the primary solvent, and modern formulations include binders and co-solvents that improve film formation. They perform best on films with sufficient surface energy—commonly achieved with corona or plasma treatment—and require controlled drying through hot-air tunnels or IR-assisted dryers to remove water without causing film distortion. The main limitations are adhesion to untreated polyolefins and sensitivity to high humidity during storage and printing; effective ink selection involves pairing with proper surfactants, coalescents, and adhesion promoters when necessary. When production lines prioritize sustainability and regulatory compliance, water-based flexo inks are a strong candidate provided the press includes adequate surface treatment and drying capacity.
These operational constraints segue to scenarios where solvent-based flexo inks are preferred because of their adhesion and drying characteristics.
Solvent-based flexo inks use organic solvents—alcohols, esters, and ketones—to achieve low-viscosity, fast-drying films with strong adhesion to a wide range of non-porous substrates, including metallized and untreated polyolefins. The rapid solvent evaporation allows printers to run at higher web speeds with less risk of set-off, producing robust films that withstand downstream conversion such as lamination and pillow-pack forming. However, solvent systems increase VOC emissions, require ventilation and solvent-recovery or abatement solutions, and may raise workplace safety considerations; compliance planning and training become part of the workflow. Typical applications include high-speed flexible packaging lines and specialty runs where adhesion and durable rub resistance outweigh VOC concerns.
The discussion of flexo ink families leads naturally into the gravure chemistries used for flexible packaging, where resolution and color strength have greater impact.
Gravure inks for flexible packaging mirror the same three core chemistries—water-based, solvent-based, and UV-curable—but are formulated for gravure-specific needs such as very low viscosity for cell transfer, high color strength for solid areas, and excellent levelling for consistent dot gain. Gravure demands inks that can quickly release from engraved cells and form a stable film on non-absorbent substrates while supporting high-resolution printing. The choice of gravure ink family is driven by end-use: high-resolution shrink sleeves and labels often favor solvent or UV systems for vibrancy and durability, while food-contact applications push toward specialized water-based gravure inks with validated raw materials. Below is a compact comparison of gravure ink types highlighting core properties.
| Ink Type | Adhesion & Color Strength | Drying/Curing Method | Food-Safety Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water-based gravure | Moderate adhesion; good regulatory profile | Evaporation with robust dryers | High, when formulated with compliant raw materials |
| Solvent-based gravure | Strong adhesion and color density | Solvent evaporation; fast set | Conditional; requires solvent controls and testing |
| UV-curable gravure | Very high gloss and durability | Instant UV polymerization | Good (low migration) if formulated for packaging |
This comparison shows gravure-specific trade-offs, leading into a closer look at water-based gravure characteristics and operational adaptations.
Water-based gravure inks are engineered to very low viscosities and include co-solvents, low molecular-weight binders, and film-formers that enable clean cell transfer and adequate wetting on treated films. They offer regulatory advantages for food-contact packaging because modern formulations can use approved raw materials that minimize migration risks, but they typically require films to be corona-treated and drying tunnels robust enough to ensure complete water removal at production speeds. Machine parameters—doctoring, cell volume selection, and nip settings—must be tuned to prevent pitting or mottling, and drying aids or IR assist can enhance speed without over-baking the film. When environmental compliance and worker safety are priorities, water-based gravure inks become an attractive option, provided the press line is configured for high-efficiency drying.
Understanding instant-cure alternatives helps explain why many converters choose UV-curable gravure for high-throughput, high-quality runs.
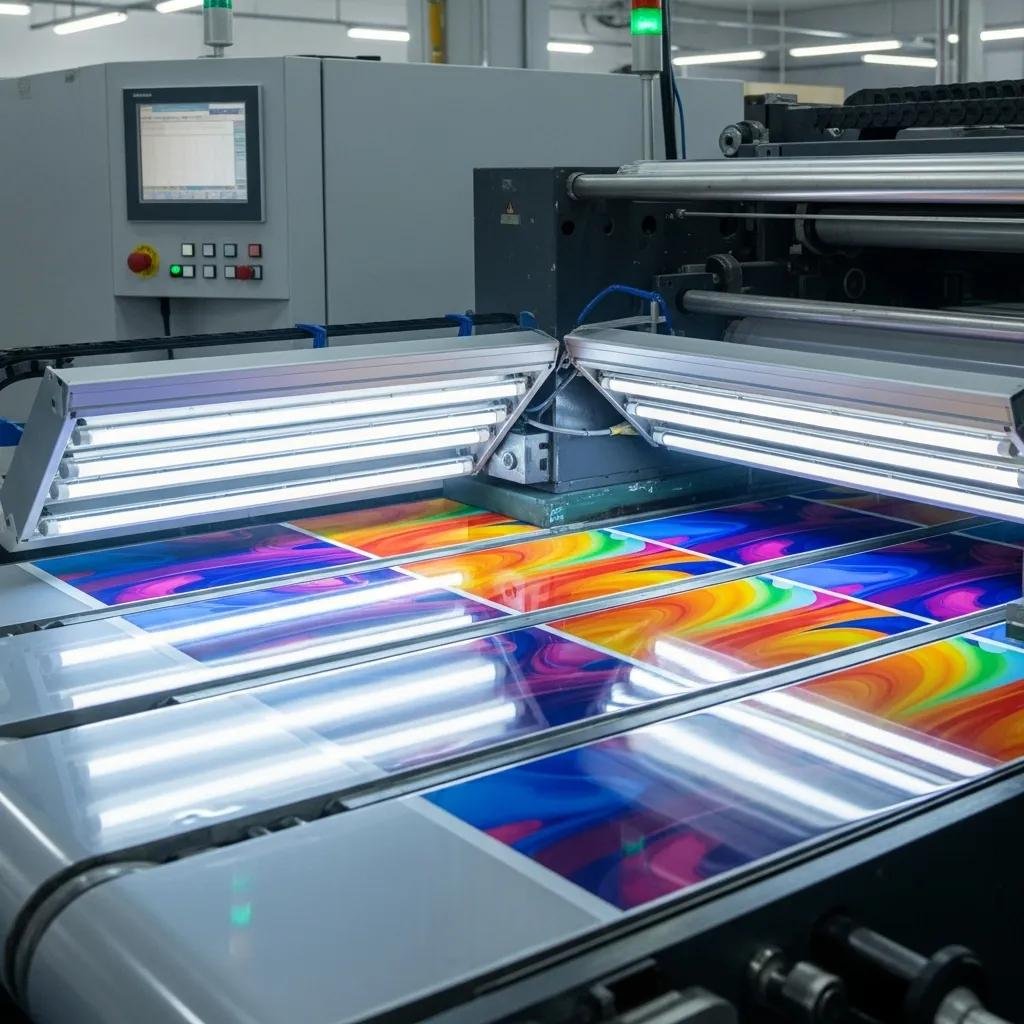

UV-curable gravure inks polymerize immediately under ultraviolet energy, enabling near-instant fixation of ink films with high gloss, excellent rub and chemical resistance, and minimal solvent emissions, which reduces VOC-related compliance burdens. The immediate cure supports very high web speeds and rapid downstream converting because inks do not have to dry by evaporation, but implementation requires matched UV lamp energy, correct ink photoinitiator systems, and attention to substrate heat tolerance to avoid distortion. UV systems also reduce migration risks associated with volatile solvents and can produce more consistent dot structure for fine-detail gravure work, although lamp aging, reflector cleanliness, and ink formulation control are critical operational factors. For lines targeting maximum throughput and premium finish, UV-curable gravure inks provide a compelling performance envelope when integrated with appropriate curing hardware.
These gravure and flexo chemistry overviews set the stage for a selection framework that prioritizes substrate, drying, durability, and regulatory constraints.
Selecting the correct ink requires balancing substrate chemistry, surface treatment, drying or curing capacity, end-use durability, and regulatory constraints; each factor directly influences adhesion, printability, and final package performance. Substrate compatibility is foundational: low-energy polyolefins like PE and PP often need corona treatment or primer coatings to accept many water-based inks, while PET and metallized films offer higher energy and often accept a wider range of chemistries. Drying and curing capabilities must match press speed—evaporative systems demand long dryer lengths or high-temperature tunnels, whereas UV-cure demands matched lamp power and dwell time to ensure full polymerization. Durability needs—abrasion resistance, chemical contact, shelf life—drive resin choices and post-print treatments such as overprint varnish or lamination. Regulatory drivers, particularly for food-contact packaging, require validated raw materials, migration testing, and documentation from ink suppliers.
Consider these selection checkpoints before specifying an ink:
This checklist helps bridge chemistry to equipment needs, which is why press features often determine the practical ink choices on a production line.
Introductory note on equipment linkage: machine features such as inline corona, adjustable ink stations, robust web handling, and modular drying or UV units directly influence which ink chemistries are feasible at scale. Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. supplies a range of printing and converting equipment whose design options—like optional drying units and corona treatment modules—can be matched to the ink workflows discussed above; converters should consult equipment specifications and request configurations that support their chosen ink family and production speeds.
Below is a substrate-focused comparison table that maps common films to surface energy needs and recommended ink families.
| Substrate | Typical Surface Energy | Typical Pretreatment | Recommended Ink Families |
|---|---|---|---|
| PE (LDPE/MDPE) | Low (requires higher dyne) | Corona or primer | Solvent-based, UV, or treated-compatible water-based |
| PP | Low-to-medium | Corona or plasma | Solvent-based or UV for untreated; water-based if treated |
| PET | Medium-high | Often no pretreat | Water-based, solvent-based, UV |
| BOPP | Medium | Corona recommended | Solvent-based and UV favored; water-based if treated |
| Nylon | Medium | Corona helps | Solvent-based or UV provide robust adhesion |
This table clarifies common substrate requirements and leads into how machine features support these choices in practice.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) manufactures flexo and gravure printing machines and related converting equipment with features that support a range of ink workflows. Machines equipped with modular drying tunnels, optional UV-curing units, inline corona treatment, and precise metering systems enable printers to adopt water-based, solvent-based, or UV-curable inks as production needs demand. The company’s product range—blown film machines, plastic bag manufacturing machines, flexo printing machines, and gravure printing machines—reflects a one-stop approach from innovation to mass production, and their equipment options include capabilities that reduce ink defects such as poor adhesion, mottling, and set-off through controlled web tension and accurate doctoring.
Practical machine-ink compatibilities are described below so converters can align ink selection with press capabilities and service expectations.
These compatibility considerations imply that proper maintenance and operator training are vital for consistent ink performance and longevity of both prints and equipment.
Routine maintenance and operational discipline significantly reduce ink waste, misprints, and downtime; a focused checklist helps keep presses running reliably. Regular cleaning and flushing schedules prevent pigment buildup and cross-contamination between ink colors, while scheduled inspections of doctor blades, anilox rolls, and metering devices ensure consistent ink transfer and color stability. Preventive maintenance—replacing seals, checking pump performance, and verifying dryer and UV lamp output—preserves curing efficiency and adhesion outcomes. Operator training that emphasizes correct viscosity control, ink temperature management, and diagnostic steps for adhesion testing reduces setup time and scrap rates. Kingdom Machine promotes easy maintenance design and after-sales support to help converters implement these practices and maintain consistent production.
These maintenance routines prepare operations to meet evolving regulatory and environmental requirements discussed next.
Environmental and regulatory drivers—especially VOC limits, worker safety, and food-contact rules—shape ink formulation choices and press configurations in 2024 and beyond. VOC emissions from solvent inks prompt many converters to evaluate low-VOC or VOC-free alternatives and to invest in abatement systems or switch to UV-curable or water-based chemistries where practical. Food-contact packaging requires attention to ink migration, approved raw materials, and documentation demonstrating compliance with regulators such as FDA and EFSA; selection of inks certified for indirect food contact and validated through migration testing reduces commercial risk. Sustainability trends also push adoption of lower-impact chemistries and energy-efficient curing systems, which influence equipment procurement and process design decisions across the value chain.
Key regulatory and environmental checkpoints:
This checklist ties directly into mitigation strategies for VOCs and into the final regulatory notes on food safety below.
VOCs drive both formulation and equipment investments because solvent emissions are regulated and pose workplace risks; converters must weigh production speed against environmental controls when selecting inks. Choosing low-VOC solvent blends, switching to water-based chemistries where possible, or adopting UV-curable systems can reduce emissions, but each option carries trade-offs in adhesion, cure control, and capital equipment. Practical mitigation measures on press lines include ventilation improvements, solvent recovery units, solvent monitoring, and training for safe handling; these operational investments often offset compliance risk and enable higher-speed solvent-based processes to continue where required. Recent studies and industry practice in 2024 show an accelerating shift toward UV and optimized water-based solutions where substrate and product allow.
These VOC considerations lead directly into food-safety requirements, which are often the strictest drivers of ink selection for consumer packaging.
Food-contact ink selection must address migration risk, approved raw-material lists, and documented testing to demonstrate compliance with regulators such as FDA and EFSA for indirect food contact. Ink suppliers should be able to provide declarations of compliance for relevant monomers, pigments, and additives, and converters must plan migration testing under expected storage and use conditions; selecting inks with established food-packaging track records reduces the need for extensive revalidation. Practical steps include requesting supplier documentation, specifying barrier coatings or laminates where necessary to prevent migration, and integrating testing into supplier qualification processes. By prioritizing inks and suppliers that produce clear compliance documentation, converters can reduce regulatory risk and protect brand safety.
These regulatory precautions conclude the technical guidance and invite converters to align equipment procurement and service partnerships with ink and substrate strategies—contact Kingdom Machine by name to discuss machine configurations, customization, and demonstrations that support compliant, efficient ink workflows.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;