Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.
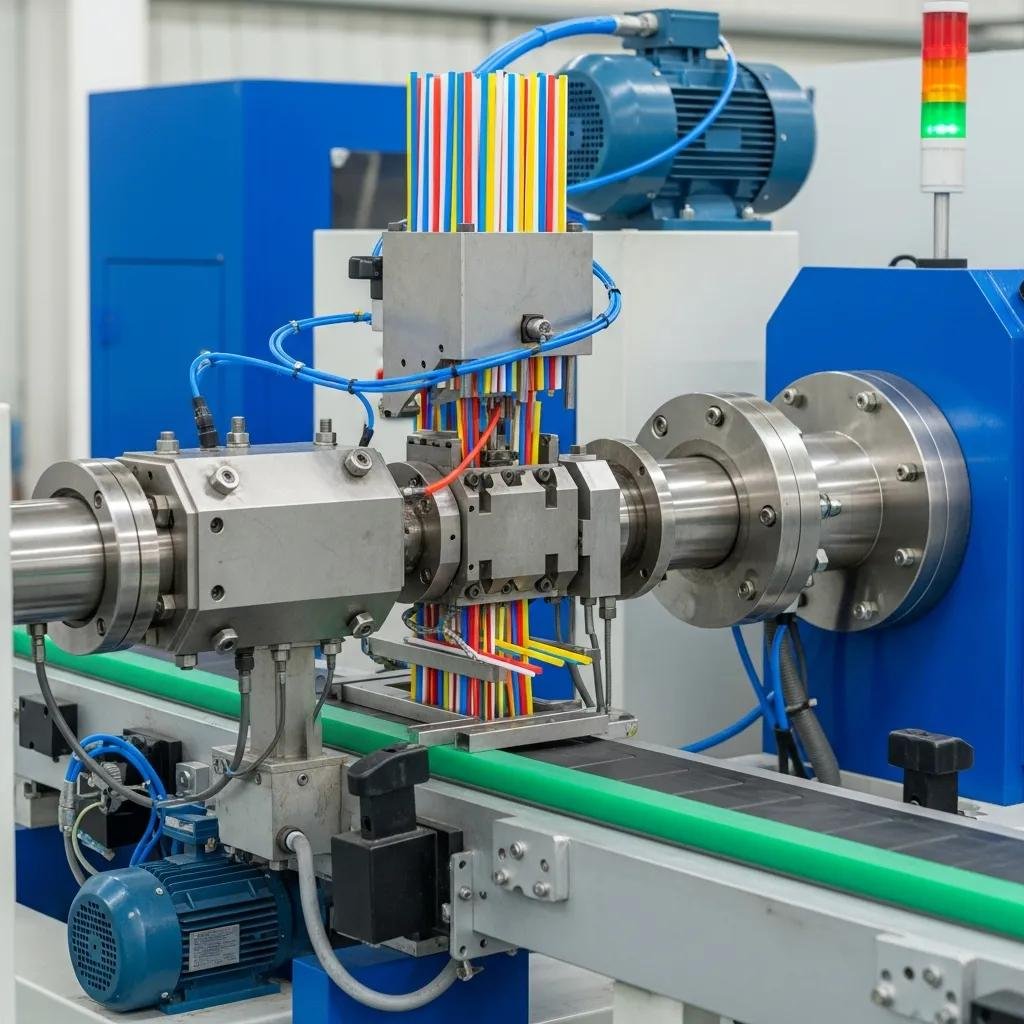
High-speed plastic drinking straw production equipment automates extrusion, cooling, and cutting to deliver high throughput—often able to reach or exceed 1,000 pcs/min—while preserving dimensional accuracy and repeatable part quality for commercial manufacturers. This guide explains what defines a high-speed straw extruder, the materials and machine architectures that enable consistent output, and the tradeoffs between PP and biodegradable options such as PLA. Many manufacturers face pressures to increase throughput, reduce labor, and respond to shifting material costs and sustainability mandates; modern automatic straw production lines address these challenges through advanced screw design, PLC control, and integrated downstream systems. Readers will learn core machine features, a step-by-step extrusion and cutting workflow, comparisons of PP versus PLA production, quality and after-sales considerations, market and pricing drivers, and a practical buyer’s checklist for selection and customization. The content integrates vendor service attributes selectively to help connect technical choices with real-world supplier strengths while keeping the focus on technical decision-making and process design.
High-speed plastic drinking straw machines are industrial extrusion systems designed to melt and shape polymer feedstock into continuous tubes that are cooled, cut, and finished at commercial throughput rates. These systems combine a high-performance extruder (screw and barrel), calibrated die head, cooling and sizing tank, cutting unit, and automated take-up/packaging modules, with PLC/servo controls to maintain dimensional tolerances and fast changeovers. Key performance metrics include production speed (pcs/min), straw diameter and length flexibility, energy consumption per kg of product, and automation level for inline quality control. The design focus is on repeatability and low scrap while enabling multi-color or flexible straw options through color feeders and specialized die tooling. Understanding these components and metrics allows buyers to match machine capability to product mix and volume expectations.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. and China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. position their production equipment around simple operation, easy maintenance, and consistent performance, backed by 100% final inspection and targeted warranty coverage on specific components. Their supplier profile highlights timely after-sales service and global machine installations, making them a candidate for buyers seeking established manufacturer support. This vendor snapshot helps manufacturers evaluate whether a supplier’s service model aligns with production reliability goals while the technical selection remains the primary focus.
This definition and vendor context lead naturally to how an automatic production line sequences material handling, extrusion, cooling, and cutting to sustain high throughput and quality.
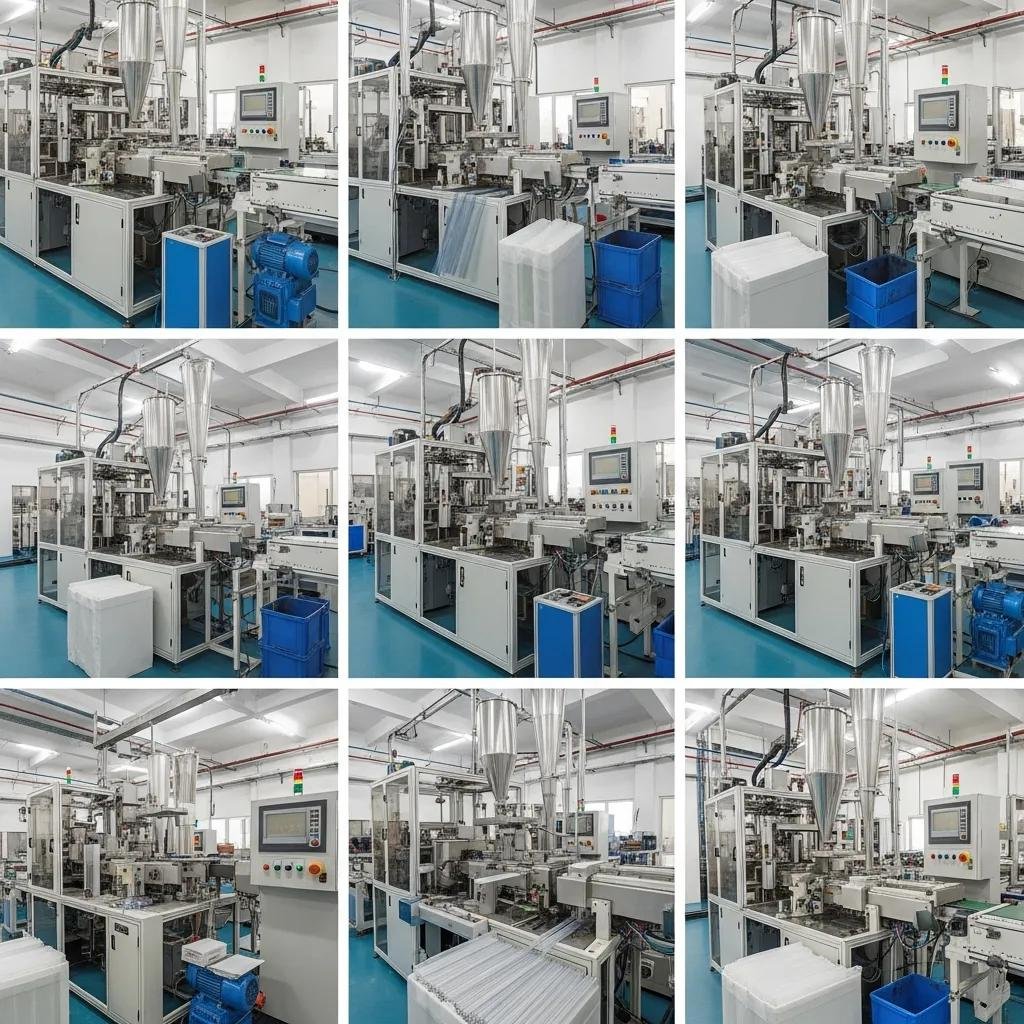

An automatic plastic straw production line operates by converting polymer pellets into finished straw segments through a tightly controlled sequence of material handling, melting, shaping, sizing, and cutting. Material is metered from hoppers into the extruder, where screw design and barrel zones control melt homogeneity and throughput; the molten polymer flows through a die that defines tube diameter, then enters a calibration and cooling stage to lock dimensions. Integrated PLC controls and servo-driven feeders synchronize line speed with cutter and take-up systems, enabling precise length control and rapid changeovers. Inline sensors and simple vision or dimensional checks reduce scrap by detecting deviations early and prompting automatic adjustments. Efficient operation therefore relies on coordinated mechanical design, responsive controls, and robust material handling to maintain continuous, high-speed output.
This operational overview prepares the reader to evaluate which raw materials are compatible with these high-speed lines and what processing considerations each material imposes.
High-speed straw extruders commonly process polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polylactic acid (PLA), and other biodegradable resins such as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) when appropriately configured for each polymer’s processing profile. PP and PE are robust, forgiving to process variations, and support high-speed extrusion with lower sensitivity to moisture, while PLA and PHA require careful feedstock handling—often drying or controlled storage—to avoid hydrolytic degradation and inconsistent melt behavior. Additives and color masterbatches enable opaque or multi-color straws but can affect melt viscosity and die pressure; therefore screw geometry and die design are chosen to accommodate formulation changes. Material choice drives downstream settings—cooling tank behavior, vacuum sizing, and cutter speed—so compatibility consideration should include supply stability, cost, and sustainability goals.
Material processing characteristics naturally lead into a comparison between PP and PLA in performance, cost, and sustainability tradeoffs.
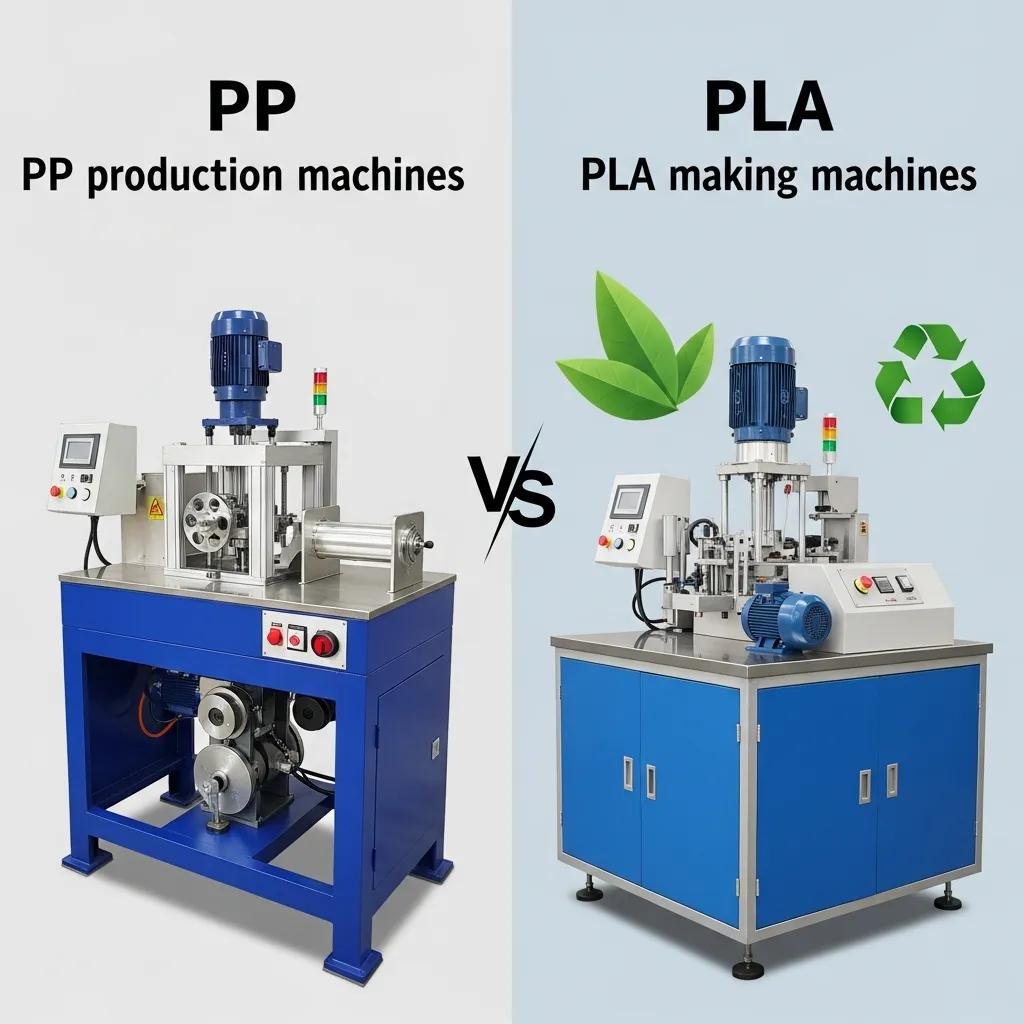

PP and PLA straw making machines are differentiated mainly by processing stability, throughput potential, and lifecycle environmental tradeoffs. PP-based lines typically offer higher processing stability, faster throughput, and lower sensitivity to moisture, resulting in lower scrap rates and simpler logistics. PLA-compatible lines require additional handling and precise melt control to avoid degradation; they often include features such as enhanced drying, tighter temperature regulation, and more frequent quality checks. From a sustainability standpoint, PLA offers biodegradability under industrial composting conditions and appeals to eco-conscious brands, whereas PP offers lower upstream greenhouse gas emissions per kg in some supply chains and greater recyclability in established streams. Choosing between them depends on product positioning: high-volume cost-focused runs usually favor PP, while brands prioritizing end-of-life biodegradability may accept higher material and processing costs for PLA.
To make that comparison clearer, consider the practical advantages of PP-based lines and the specific adaptations PLA production requires.
PP straw making equipment excels in throughput, process tolerance, and cost efficiency, making it a common choice for large-scale production where consistent output and low per-unit cost are priorities. PP’s thermal and rheological stability allow robust screw designs and higher screw speeds without frequent process interruptions, which translates to higher achievable pcs/min and lower downtime for corrective adjustments. Lower sensitivity to moisture and simpler material storage needs reduce pre-processing requirements like drying, lowering operational complexity and utility consumption. These strengths make PP machines attractive for foodservice and high-volume private-label production where predictable OPEX and fast changeovers are critical.
This understanding of PP behavior sets the stage to contrast the specialized needs of PLA-compatible systems and why they are selected despite higher process demands.
PLA straw manufacturing machines incorporate process adaptations that handle PLA’s sensitivity to moisture and thermal history, supporting biodegradable production while striving to maintain acceptable throughput. Typical adaptations include controlled feed hoppers, optional in-line dryers, precise barrel temperature zoning, and gentler screw designs that reduce shear to prevent polymer degradation; vacuum venting can help remove volatiles. PLA’s market appeal is driven by end-of-life considerations and regulatory or brand-driven sustainability programs, but producers must manage supply volatility and higher raw-material cost. For buyers, selecting a PLA-capable line means planning for additional material handling investments and validation runs to ensure product appearance, mechanical properties, and compostability targets are met.
The detailed extrusion process in drinking straw production transforms polymer feedstock into continuous tubular product through coordinated stages: feeding and melt preparation, extrusion through a die, calibration and cooling, cutting and finishing, and packing. Each stage contributes a control point—feed consistency for throughput stability, screw and die design for wall thickness and roundness, cooling tank settings for dimensional lock-in, and cutting mechanics for end-quality and length accuracy. Inline automation synchronizes these stages to prevent bottlenecks and maintain repeatable production speed while minimizing scrap. Process control parameters and tolerances are typically mapped to product specs, enabling operators to tune production for different diameters, wall thicknesses, and flexible or straight straw variants.
Understanding these stages is best achieved via a clear step-by-step sequence and a process equipment map that clarifies tolerances and control points.
Below is a concise, numbered process sequence that outlines the core procedural steps and quality checkpoints in straw extrusion and cutting:
Each step has associated tolerances—OD/ID and length tolerances most critical—and inline sensors or periodic sample checks help maintain these targets. These steps transition naturally to the value that automation brings in achieving speed and precision.
| Process Stage | Control Point | Typical Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding & Prep | Moisture/content | Consistent feed rate; drying for PLA |
| Extrusion | Melt homogeneity | Die pressure and screw torque |
| Calibration | Cooling profile | Dimensional stability |
| Cutting | Length control | Servo timing and blade condition |
Automation—via PLCs, servo motors, and closed-loop feedback systems—reduces variability and enables sustained high-speed straw production by precisely coordinating extruder output, take-up rate, and cutting actions. Closed-loop control maintains melt pressure and line speed, automatically adjusting screw speed or haul-off to keep dimensions within tolerance; servo-driven cutters provide repeatable length accuracy with minimal mechanical wear. Remote monitoring and diagnostics allow rapid response to deviations, minimizing downtime and scrap while enabling predictive maintenance through logged trends. Automation also simplifies changeovers between diameters or materials by storing recipe parameters, which shortens setup time and helps maintain consistent quality across batches.
| Automation Component | Role | Production Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| PLC with recipes | Stores process sets | Fast, repeatable changeovers |
| Servo drives | Precise motion | Accurate length control |
| Sensors & feedback | Real-time adjustment | Reduced scrap, higher uptime |
These automation benefits tie directly to vendor capabilities and how supplier R&D or service models can accelerate line commissioning and uptime.
Kingdom Machine’s R&D emphasis on automation and a one-stop service model supports efficient commissioning and continuous improvement of extrusion lines, and their production footprint includes multiple production lines enabling relatively fast sample and bulk delivery. Their operational claims of sample delivery in 3 days and bulk orders in 15-20 days, along with a broad global installation base, can help buyers bridge technical selection with supplier logistics when validating lead times and initial trials.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. and China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. emphasize quality assurance, straightforward maintenance, and responsive after-sales service as core supplier differentiators. Their stated quality practices include 100% final inspection of finished machines to verify mechanical alignment and control function prior to shipment, and a specified warranty on timer switches for two years. The vendor also promotes simple operation and easy maintenance as part of machine design, aiming to reduce onsite complexity and training time for operators. For buyers, these supplier attributes indicate a focus on pre-shipment validation and component-level warranty coverage that can ease initial acceptance and early operation.
Framing these supplier practices naturally leads to the specific quality assurance measures implemented on straw machines and industry best-practice recommendations buyers should request.
Quality assurance for straw production equipment typically combines factory inspection protocols with defined tests for mechanical function and process validation to ensure machines meet performance targets. The supplier-validated measures include 100% final inspection of assembled machines to confirm alignment, control calibration, and basic run testing; this is complemented by recommended in-house checks such as dimensional sampling (OD/ID), tensile or bend testing for flexible straws, and visual surface inspections. Kingdom Machine’s stated offering of a two-year warranty on timer switches is an explicit component of their QA/warranty package and demonstrates targeted component backup. Buyers should document pre-shipment test runs and request recorded run sheets to match machine performance to contract specifications.
Effective maintenance and troubleshooting combine routine preventive tasks with clear escalation steps for common failure modes to maintain production continuity. Daily and weekly checks include monitoring screw wear and alignment, inspecting heater bands and thermocouples, checking cutter blade sharpness and alignment, and verifying water quality and cooling tank performance; monthly activities often address gearbox lubrication and belt tensions. Common troubleshooting steps start with verifying electrical and control signals, stabilizing melt temperature and pressure, and inspecting die and cutter wear. Having spare critical parts on hand—blades, heater cartridges, and seals—and operator training reduces MTTR and supports timely repairs. A vendor with a global service footprint and spare part availability can significantly help buyers maintain uptime by combining remote diagnostics with on-site support when required.
Current market trends in mid-2024 show steady demand growth driven by foodservice recovery, rising interest in biodegradable options, and automation adoption to reduce labor and improve consistency. Key pricing factors for straw extruders include raw-material selection (PP vs PLA), machine capacity and automation level, required certifications, and customization such as multi-color feeders or flexible straw tooling. Regions with strong manufacturing ecosystems—particularly in Asia—continue to drive competitive machine pricing and export capacity. Buyers should consider not only machine CAPEX but also operational cost drivers such as energy consumption, spare-part availability, and expected throughput when calculating total cost of ownership.
The following table summarizes common market and price drivers to help buyers prioritize decision factors.
| Market Driver | Attribute | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Material type | PP vs PLA | PLA increases CAPEX/OPEX due to drying/handling |
| Automation level | Basic → Advanced | Higher automation raises upfront cost but reduces labor |
| Capacity | pcs/min capability | Higher-capacity machines cost more per line but lower per-unit cost |
| Customization | Multi-color/unique dies | Adds tooling and setup cost; increases lead time |
Material choice strongly influences both machine configuration and ongoing costs: PLA requires dryers, tighter temperature control, and more frequent quality sampling, which increases initial CAPEX and operating complexity compared with PP. PLA’s raw-material price volatility and supply-chain sensitivity can drive operational cost uncertainty, raising total cost of ownership even if per-piece processing is optimized. Conversely, PP’s lower raw-material cost and simpler storage reduce operational overhead, but end-of-life disposal or regulatory pressure can alter long-term economics. When estimating price implications, factor both machine modifications required for a polymer and longer-term material supply/pricing risks.
Recent industry analyses indicate continued growth in production equipment demand as foodservice activity and sustainable packaging initiatives increase demand for both conventional and biodegradable straws. Forecasts point to steady CAGR figures for extrusion and converting equipment through the next decade, with regional strength concentrated in Asia-Pacific manufacturing hubs that supply global markets. This growth implies that buyers may encounter varying lead times depending on production capacity and customization requests, making early engagement with suppliers and clear specification sheets increasingly important. Anticipating market trends helps buyers time purchases to avoid peak lead-time windows and to secure materials and tooling aligned with production forecasts.
Selecting and customizing high-speed straw extrusion machines requires a structured evaluation of production targets, product specifications, material compatibility, automation level, and vendor support. Start by defining required throughput (pcs/min), straw types (straight, flexible, multi-color), material choice (PP, PLA), and acceptable tolerances for diameter and length. Evaluate automation features—recipe storage, servo cutters, and inline QC—and map these against floor-space, power availability, and budget to determine the appropriate machine class. Customization options such as additional color feeders, interchangeable die sets for diameter changes, and automated packaging modules enable product variety but add cost and may extend lead time; weigh these against expected SKU volumes and ROI.
Below is a comparison table to help buyers map typical machine options to production needs.
| Machine Option | Characteristic | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Basic line | manual setup; simple control | Small batch production, low automation needs |
| Mid-level | PLC recipes; servo cutter | Medium throughput with frequent product changes |
| High-capacity | Advanced automation; multi-color | High-volume production, multi-SKU runs |
Common customizable features in straw production lines include interchangeable die tooling for different outer diameters, multi-color masterbatch feeders for striped or multi-color straws, servo-driven cutting units for tight length tolerances, and downstream packaging integration for automated bagging or cartoning. Each customization affects lead time and cost: adding color feeders requires additional control integration and color change protocols, while bespoke die sets necessitate careful flow simulation and validation. Buyers should prioritize customization that directly supports product differentiation or operational efficiency and avoid one-off features that complicate maintenance or raise spare-part burdens.
Choosing the correct model follows a stepwise decision flow: define the product specifications (diameter, length, flexibility), set throughput targets and shift structure, confirm material(s) and handling requirements, determine necessary automation and QC features, and then request vendor data sheets and test-run evidence to validate claims. Ask vendors for recorded sample runs with your material and product specs, references from similar installations, and a breakdown of spare parts and recommended preventive maintenance schedules. Use an EAV-style comparison to quantify tradeoffs—throughput vs cost, automation vs flexibility—to calculate payback periods and expected per-unit costs.
| Selection Criteria | Attribute | Buyer Question |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | pcs/min | Does the model meet peak production? |
| Material compatibility | PP / PLA | Can the line handle planned resins reliably? |
| Automation | PLC/servo | Will automation reduce labor and scrap? |
This decision framework, combined with vendor test data and a clear maintenance plan, enables buyers to select a model that aligns with production goals and long-term cost management.
For vendors like Kingdom Machine, their global installation record and one-stop service approach can shorten validation cycles; their stated delivery cadence—samples in 3 days and bulk lead times of 15-20 days—may help manufacturers plan pilot runs and scale-up timelines while ensuring access to spare parts and training where needed.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;