Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.
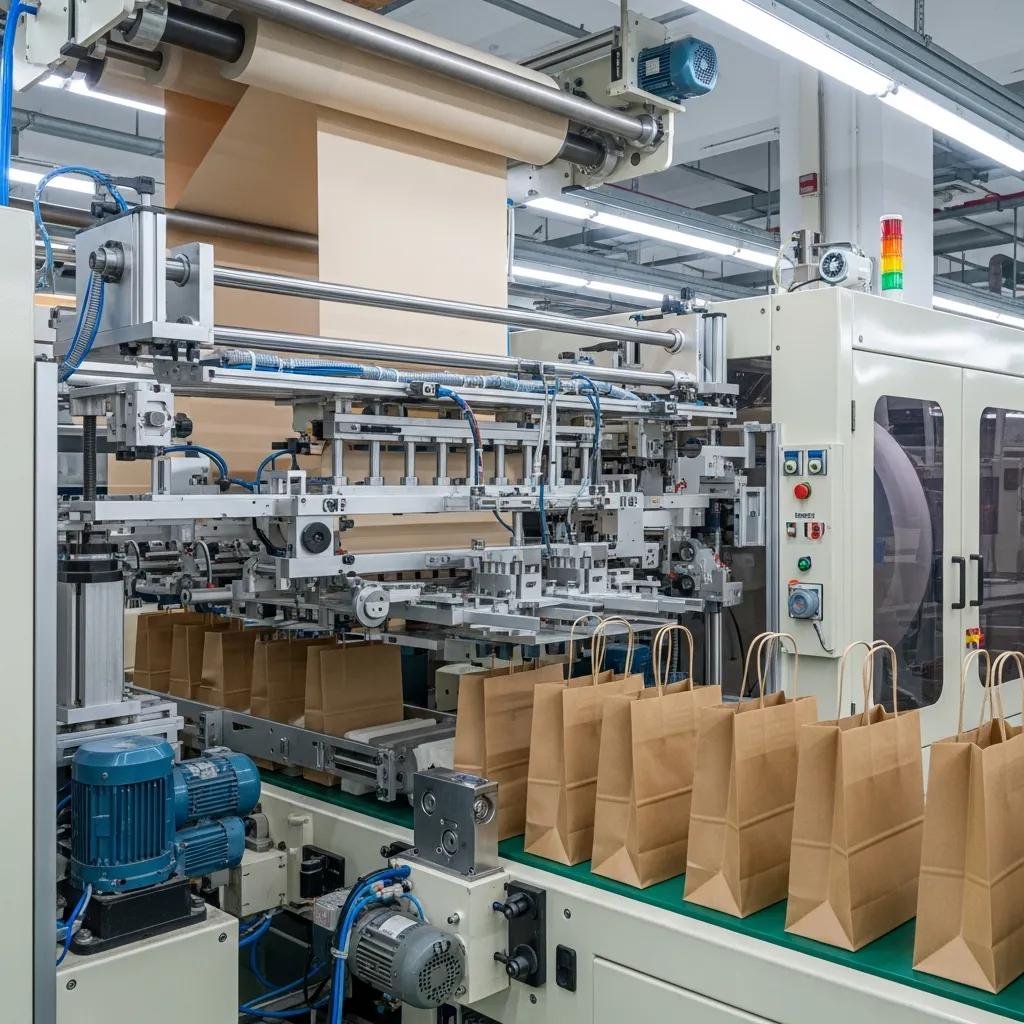

Automated square bottom paper bag machines with handles form a specialized class of bag making machinery that converts roll-fed paper into finished square-bottom shopping bags while integrating handles inline for high-throughput, consistent output. These fully automatic systems mechanize roll feeding, tube forming, bottom creasing, gluing, cutting and handle attachment to deliver durable paper shopping bags suited to retail, food service and e-commerce applications. Manufacturers choose these machines to increase production capacity, improve quality consistency and support sustainable packaging strategies by using kraft or recycled paper grades. This guide explains what these machines do, which technologies enable high-speed production, how different handle methods affect bag functionality, where the machines are applied in industry, how to optimize efficiency and sustainability, and what buyers should evaluate before investing. Readers will learn practical technical criteria—servo vs mechanical drives, PLC recipe control, inline handle units—and procurement advice to match machine class to required throughput and bag specifications. The article integrates vendor selection and lead-generation pathways without overshadowing technical depth, ensuring you can move from specification to sourcing with confidence.
A fully automatic square bottom paper bag machine with handles transforms roll paper into finished square-bottom bags in a single continuous process by feeding web stock, forming a tube, creating creased bottoms, applying glue, cutting to length and attaching handles inline. The mechanism reduces manual handling and delivers stable throughput with consistent bag dimensions and glued joints, producing bags across a range of GSM papers and sizes for retail or food use. Typical throughput varies by model and specifications, with many high-speed machines delivering dozens to hundreds of bags per minute depending on bag dimensions, handle type and paper weight. The inline handle capability supports twisted rope, flat belt and die-cut options, each compatible with specific paper types and adhesive systems. Understanding these production steps clarifies subsequent sections on feature selection, handle integration trade-offs, and technology choices that determine speed and quality.
Automated paper bag machines combine several ergonomic components—servo motor systems, PLC control units, gluing system, cutting unit, web guide system and handle attachment unit—into an integrated production line that prioritizes repeatability and low downtime. Servo-driven systems enable precise position control for cutting and handle placement, while PLCs store recipes for rapid changeovers between bag sizes and handle formats. Roll-fed designs support continuous production with simplified material handling and lower scrap rates relative to sheet-fed approaches, and inline quality inspection systems ensure glued seams and handle attachments meet tolerances. Common metrics include bag throughput ranges, typical GSM compatibility (e.g., kraft paper 80–200 GSM), and creasing/pleating capability for square bottoms. These features collectively reduce operator intervention and make these machines suitable for mid-to-high volume manufacturing, which leads naturally to selecting specific technologies that enhance speed and consistency.
Handle choice directly affects bag strength, consumer perception and production complexity, and the three main handle families are twisted rope, flat belt and die-cut. Twisted rope handles deliver high tensile strength and a tactile, premium feel that suits luxury retail bags but require robust inline attachment and often slower attachment cycles than flat belt systems. Flat belt handles offer a cost-effective balance of appearance and load-bearing capacity for apparel and mid-range retail, while die-cut handles minimize material use and present a clean aesthetic that pairs well with compact, stackable bags for takeaway and light grocery use. Handle selection also influences adhesive type, attachment spacing and reinforcement needs; therefore the manufacturing specification must align handle method to end-use requirements before finalizing machine options.
High-speed production of square bottom paper bags with handles relies on a combination of precision motion control, intelligent automation and robust web handling to maintain quality at increased line speeds. Key technologies include servo motor systems for accurate positioning, PLC and HMI control for recipe management and diagnostics, roll-fed continuous supply systems for sustained throughput, and web guide and tension control to prevent misfeeds and reduce scrap. These technologies interact: precise tension control prevents registration errors that would otherwise force slower line speeds, while PLC-driven recipe storage minimizes changeover time between bag formats. The next paragraphs break down how servo/PLC systems and roll-fed architectures each contribute to throughput and operational efficiency.
This table compares servo, mechanical and hybrid control approaches and their production impact.
| Control System | Characteristic | Impact on Speed & Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Servo drive system | Electronic position and speed control with closed-loop feedback | Enables high accuracy and faster changeovers, improving throughput and consistent handle placement |
| Mechanical/cam drive | Fixed cam profiles and mechanical timing | Lower initial cost but limited flexibility and slower adjustment for varied bag sizes |
| Hybrid (servo + cam) | Cam for coarse timing, servo for fine adjustments | Balances cost and precision for medium-speed lines with intermittent high-accuracy needs |
Servo motors plus PLC control systems provide the decision-making and motion precision needed to synchronize web feeding, cutting and inline handle attachment while keeping setup and changeover times short. Servos control precise indexing and timing at the handle attachment unit and knife station, reducing registration errors and minimizing adhesive misalignment that leads to rejects. PLCs with HMI enable operators to store bag size recipes and torque or glue parameters, so switching between formats becomes an operator-driven selection rather than lengthy mechanical reconfiguration. From a maintenance standpoint, servos require electrical expertise but reduce mechanical wear compared with cam-based systems, shifting preventive work toward software diagnostics and sensor checks.
Roll-fed architectures supply continuous web paper to the forming section, which maintains steady production cycles and eliminates the per-sheet handling delays inherent to sheet-fed machines. Continuous feeding reduces downtime and scrap associated with loading pre-cut blanks and improves material logistics for high-volume runs, translating to lower per-unit labor costs and more predictable throughput. For long runs of a consistent bag format—such as retail shopping or grocery bags—roll-fed machines are markedly more efficient and simplify upstream material procurement. The operational simplicity and throughput advantages of roll-fed machines make them the preferred choice for large-scale production environments seeking energy efficiency and predictable output.

Handle integration method is a key determinant of finished bag tensile strength, appearance and the complexity of the production process, and it directly influences cycle times and scrap rates. Inline handle units that attach pre-made handles or form and attach handles from supplied material can be synchronized with the main forming line but introduce additional timing and adhesive complexity. Pre-made handle systems can speed some operations but require accurate placement and increased inspection, while die-cut handles reduce material use but may require secondary reinforcement or backing layers for load-bearing applications. The trade-offs between aesthetics, load capacity and production cost must be evaluated relative to bag use-case to choose the right handle integration method.
Twisted rope and flat belt handle solutions present different balances of strength, cost and production speed, and selecting between them depends on product positioning and functional needs. Twisted rope handles provide superior load-bearing capacity and a premium look, which suits luxury retail or heavy items, but they often need more complex attachment fixtures and slower indexing to secure the rope ends. Flat belt handles are simpler to source and attach, offering reasonable strength for most retail bags and faster application cycles that favor higher throughput. For many operations, flat belt handle machines deliver a cost-effective compromise, while twisted rope systems are chosen when brand perception and higher load performance are essential.
Die-cut handles are formed directly in the bag body, offering a seamless aesthetic and minimizing external handle material, which reduces per-unit material cost and packaging complexity. Tooling and die maintenance are important considerations: initial die fabrication increases capital cost, and regular sharpening or replacement is necessary to maintain clean cut edges and prevent ragged openings. Die-cut is best for high-volume, space-conscious applications where a clean look and low material overhead are priorities, and the method pairs well with reinforced bottom designs to preserve stacking stability under load. Manufacturers should weigh tooling amortization against per-unit savings when deciding if die-cut handle solutions fit their cost models.
Square bottom paper bags with handles serve retail, food packaging and e-commerce markets where branding, load stability and sustainability are increasingly influential purchase drivers. In retail, bags function as a touchpoint for brand presentation and often prioritize handle aesthetics and print quality; food packaging demands grease-resistant liners and safe adhesives, while e-commerce requires bags that resist crushing during shipping and support stacking. Market trends in 2024 show rising demand for recyclable and recycled paper solutions, regulatory pressure limiting single-use plastics, and growth in branded retail packaging that favors customizable handle and print options. These market drivers convert directly into procurement needs for machines capable of handling specific paper grades and finishing options.
Different verticals impose distinct technical requirements on bag machines: retail often demands higher print registration and handle aesthetics, food packaging emphasizes food-safe adhesives and grease barriers, and e-commerce favors durable bottoms and reinforced handles for transport. For example, bakeries need grease-resistant liners and compact die-cut handles, apparel retailers look for twisted or flat belt handles that match luxury presentation, and online merchants prioritize stacking stability to reduce damage in transit. Operators should match machine capabilities—such as printable web alignment accuracy, glue system precision and handle reinforcement options—to the target application before committing to a purchase.
Global demand for paper bag production equipment is rising due to stricter plastic regulations in many regions and growing consumer preference for sustainable packaging, prompting investments in machines that support recycled kraft and lower-energy operation. Recent market analyses indicate steady CAGR for paper packaging equipment, driven by retail and e-commerce growth and regulatory shifts that favor paper over plastic. Innovation trends include energy-efficient drives, predictive maintenance systems and modular inline units that enable rapid adaptation to new bag formats. These trends emphasize that purchasing decisions should consider not only current capacity needs but also future regulatory and sustainability requirements.
Operational efficiency and sustainability in square bottom paper bag production are achieved by aligning material selection, process tuning and machine features to reduce scrap, energy use and lifecycle impact while maintaining throughput. Key strategies include precise web tension control to avoid misfeeds, optimizing glue application to minimize excess adhesive, implementing inline inspection to catch defects early, and selecting energy-saving components like inverter drives and efficient heaters. Material choices—recycled kraft, appropriately selected GSM and eco-friendly adhesives—reduce lifecycle footprint and simplify end-of-life recycling. The following sections provide actionable tuning tips and material comparisons to guide practical improvements on the shop floor.
This table compares paper types and sustainability metrics to help match material selection with machine settings and waste expectations.
| Paper Type (GSM) | Recyclability | Recommended Machine Settings |
|---|---|---|
| Recycled kraft (80–120 GSM) | High | Lower glue volume, moderate tension, slow initial speed for tuning |
| Virgin kraft (100–160 GSM) | High | Standard glue settings, higher speeds possible with good tooling |
| Coated/grease-resistant (120–180 GSM) | Moderate | Use food-safe adhesives, adjust creasing pressure, test cutter settings |
Concrete tuning steps reduce scrap and maximize throughput: calibrate and log web tension parameters for each paper GSM, fine-tune glue application to the minimum effective bead, and standardize quick-change fixtures to cut changeover time. Implement inline quality checks—such as seam-bond verification and handle-placement sensors—to detect defects before they accumulate into larger rejects, and employ predictive maintenance schedules based on runtime metrics to prevent sudden downtime. Training operators on recipe selection and quick troubleshooting reduces human error and improves overall equipment effectiveness. These operational improvements create a virtuous cycle: fewer rejects free capacity for more production and reduce per-unit energy and material use.
This table contrasts material sustainability and machine advice to support eco-focused production decisions.
| Material Attribute | Sustainability Metric | Machine Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclability | High for uncoated kraft | Use optimized glue profiles and minimal coatings |
| Adhesive type | Biobased adhesives lower impact | Test compatibility with glue unit and drying system |
| GSM selection | Lower GSM reduces material use but may need reinforcement | Adjust creasing and bottom-crease pressure accordingly |
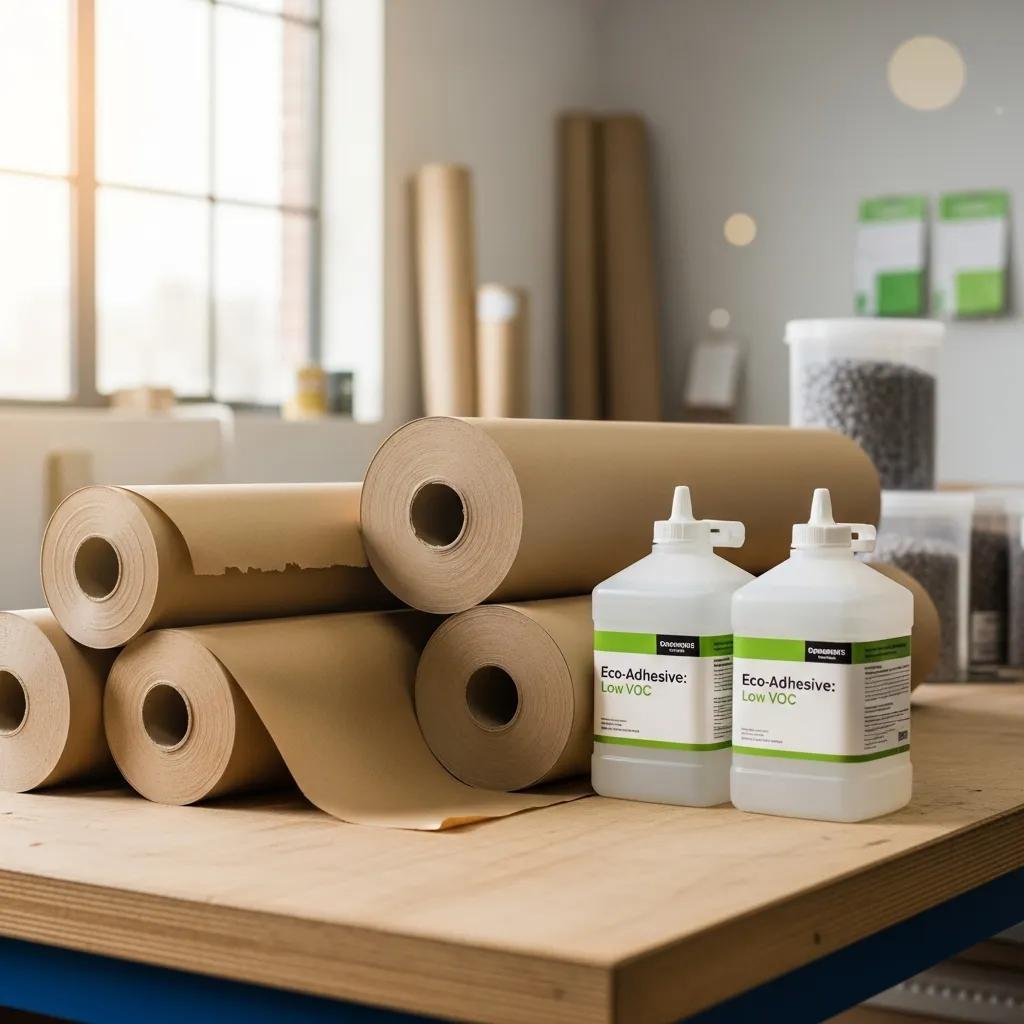

Selecting recycled kraft paper and low-VOC, water-based adhesives decreases lifecycle impact and facilitates downstream recycling, but machines must be validated for those materials to ensure reliable glue bonds and creasing. Energy efficiency can be gained through inverter-driven motors, optimized heater control for hot-melt systems and idle-power reduction strategies in PLC logic. Certifications and compliance—such as food-contact suitability for adhesives—should be verified during procurement to avoid retrofitting later. Combining material choices with energy-saving machine options and operator best practices yields measurable reductions in both operating cost and environmental footprint.
Investing in automated paper bag machinery requires evaluating total cost of ownership, expected payback, machine capability to meet bag format and handle requirements, spare parts availability, warranty terms and the vendor’s ability to support customization and timely service. Total cost calculations should include capital expenditure, operating costs (energy, adhesive, labor), projected throughput-derived revenue gains and spare-part provisioning. Buyers should request test reports and inspect quality assurance processes to validate claims about defect rates and warranty coverage. The next subsections present an ROI framework and vendor selection checklist to guide procurement decisions.
A practical ROI model compares machine classes by capital cost, throughput (bags per minute), operating cost per hour and estimated payback period based on production volume and unit margin. Consider sensitivity: increased material costs or slower-than-expected uptake can lengthen payback, while labor savings and reduced rejects accelerate it. Below is a simplified EAV-style comparison to illustrate typical trade-offs between compact, mid-speed and high-speed systems.
| Machine Class | Capital Cost | Throughput (bags/min) |
|---|---|---|
| Compact entry | Lower capital | 20–50 |
| Mid-speed roll-fed | Moderate capital | 50–150 |
| High-speed automated | Higher capital | 150+ |
When selecting a vendor, prioritize verification of quality assurance processes, warranty terms, spare-parts supply and the capacity for one-stop customization so your machine can be adapted to unique handle or print requirements. Confirm testing procedures, acceptance inspection protocols and the vendor’s R&D capability to support future upgrades, and clarify lead times and logistics for spare parts to avoid extended downtime. Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. positions itself as a manufacturer and supplier offering simple operation, perfect performance, easy maintenance, timely after-sales service, quality assurance (100 percent final inspection, 1–3 percent defective products, two-year warranty on timer switches), strong R&D, one-stop customization service, strong production capacity, competitive prices, and fast delivery. Prospective buyers can request a quote, download a product catalogue or submit an inquiry form to start discussions about customized machine specifications and delivery timelines.
This final section reiterates procurement actions and invites commercial engagement in a concise call-to-action that preserves the article’s technical focus. The combination of servo-driven motion, PLC recipe control, roll-fed continuous feeding and appropriately selected handle integration yields production lines that meet modern sustainability and throughput targets. Operational tuning—web tension, glue profiles, inline inspection—and selecting recyclable paper grades significantly reduce waste and improve ROI. For vendors, Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. offers manufacturing and supply capabilities that emphasize simple operation, reliable performance, easy maintenance and timely after-sales service; the company also highlights quality assurance (100 percent final inspection, 1–3 percent defective products, two-year warranty on timer switches), strong R&D, one-stop customization, high production capacity, competitive pricing and rapid delivery. To explore options, request a quote, download a machine catalogue or submit an inquiry form to initiate specification discussions and performance testing.
These final pointers align purchasing decisions with operational realities, enabling buyers to convert market demand for sustainable, branded packaging into efficient manufacturing throughput.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;