Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

High-speed slitter rewinder machines convert large-format webs of film and paper into finished rolls by unwinding a parent roll, precisely slitting the web to target widths, and rewinding the narrower rolls for downstream converting. This guide explains how these machines work, classifies the main machine types, and maps advanced technologies—like automatic tension control, servo-driven positioning, and PLC integration—to measurable production benefits. Manufacturers and converters facing throughput limits, inconsistent roll quality, or excessive trim waste will find practical decision criteria, specification guidance, and application examples to select the right system. The article covers operational workflows, material-specific slitting choices, typical industrial applications from flexible packaging to label stock, and a buyer’s checklist for procurement and vendor evaluation. Throughout, terms such as plastic film slitter rewinder, turret slitter, automatic tension control slitter, and razor versus shear slitting are used to build a clear semantic picture that supports purchasing and engineering decisions.
High-speed slitter rewinder machines are converting equipment designed to process wide webs at production speeds, executing a controlled sequence of unwinding, edge guiding, slitting, and precise rewinding to produce multiple finished rolls quickly. The machine synchronizes unwind tension, slitting action, and rewind torque so that slit widths and roll concentricity remain within tight tolerances, which in turn reduces downstream rejects and manual rework. Key subsystems include the unwind stand, web guide, slitting unit (razor, shear, or score), automatic tension control, and a rewind turret or multiple shafts that handle continuous or intermittent roll changes. In high-speed applications, servo motors and closed-loop tension systems maintain stable web behavior even at elevated linear speeds, preserving optical properties and printable surfaces. Understanding the sequential path and component interactions clarifies why specific machine classes are recommended for film versus paper applications and sets up the detailed process description that follows.
The slitting and rewinding workflow begins with loading a jumbo parent roll onto the unwind stand, then guiding the web through edge sensors and dancer or load-cell tension devices before the slitting station cuts the web into narrower lanes. The slitting action can be continuous or intermittent depending on turret architecture; the rewinding stage collects each slit lane onto cores with controlled torque to produce rolls with consistent diameter and core-to-edge alignment. Quality checkpoints include edge trim capture, web-surface inspection, and roll hardness checks to prevent telescoping and wrinkles. Film typically demands faster line speeds and lighter web tension than paper, so control strategies differ; these process distinctions inform blade choice, tension profiles, and rewind methods. This practical process overview leads naturally into a review of the materials commonly processed and the slitting considerations each material requires.
Slitter rewinders routinely handle a broad range of films and papers: BOPP, PET, PVC, LDPE, HDPE, laminates, foils, thermal paper, kraft paper, and nonwovens are common feedstocks in converting lines. Each material imposes unique handling requirements—metalized PET and foils need careful shear or score slitting to avoid burrs, while soft LDPE films often benefit from razor slitting and lower tension to prevent neck-in. Thermal paper and label stocks require high-precision rewind control to preserve print registration and avoid edge contamination, whereas thicker packaging paper tolerates higher line tension but needs robust blade retention and scrap trim management. Blade selection, slit pitch, and tension setpoints are chosen based on material thickness, surface finish, and downstream processing needs, which prepares the buyer to map material needs to machine classes in the next section.
High-speed slitter rewinder machines fall into several classes—center winding, surface winding, turret slitters, automatic slitting machines, and duplex or lamination-capable systems—each optimized for particular materials and production profiles. Choosing among these categories depends on target line speed, required roll diameters, slit width range, and whether continuous production through automatic roll changeover is necessary. Below is a concise classification list to orient buyers quickly before a comparative table that maps attributes to typical use cases.
High-speed slitter rewinder classifications and one-line use cases:
Different machine types suit distinct converting needs and production environments.
| Machine Type | Best for Material / Typical Max Speed | Typical Rewind Diameter | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turret Slitter | BOPP, PET, LDPE films / up to 350 m/min | 1200 mm | Continuous high-speed film converting with nonstop roll changeover |
| Automatic Slitting Machine | Narrow web films, label stock / 150–300 m/min | 600–1000 mm | High-mix, precision slit widths with auto core handling |
| Center/Surface Winder | Paper, board / 100–250 m/min | 1000–1500 mm | Paper converting where winding method controls roll hardness |
| Duplex / Lamination-Capable | Laminates, composite films / 100–300 m/min | 800–1200 mm | Simultaneous slitting and lamination for flexible packaging production |
This table highlights trade-offs—speed, diameter, and materials—so procurement teams can shortlist machine classes before evaluating specific vendors.
Plastic film slitter rewinders emphasize high line speeds, low-to-moderate web tension, and slitting methods that preserve film optics; razor slitting or shear with precise blade clearance is common to avoid surface marks. Paper roll slitting machines, by contrast, operate with higher tensions, heavier-duty unwinds and rewind shafts, and blade systems engineered for fibrous material; score slitting and reinforced knife holders are typical for thicker paper grades and kraft. Maintenance and consumable cycles differ: film lines prioritize flatness and edge cleanliness, while paper lines focus on blade durability and trim management. These engineering differences affect procurement: film converters often specify servo synchronization and dancer-based tension control, whereas paper converters may request heavier gearboxes and stronger rewind brakes. Recognizing these divergences helps buyers select appropriate core and drive components for their process.
Turret slitters deliver continuous production by transferring finished rolls from one turret position to another without stopping the web, eliminating downtime for roll changeovers and increasing effective throughput. Key features include pneumatic or hydraulic turret indexing, automatic core loading, and controlled transfer heads that protect slit edges during handoff. Automatic slitting machines bring advanced automation: motorized blade positioning, CNC knife adjustment, auto blade lifters, and PLC recipes for repeat jobs, which minimize setup time and reduce operator dependency. Both machine types often integrate web inspection and automatic tension control to ensure consistent roll quality across frequent format changes. Understanding how turret mechanics and automatic functions interact with control systems is essential when specifying uptime and labor-reduction targets for high-speed lines.
Advanced technologies enhance slitter rewinder performance by stabilizing the web path, automating critical adjustments, and providing precise motion control to meet tight tolerances at speed. Technologies to prioritize include automatic tension control (closed-loop dancers or load cells), servo-driven unwind/rewind systems, PLC-based recipe management and diagnostics, and web guiding with camera or edge-sensor feedback. These technologies collectively reduce defects such as telescoping, wrinkles, and variations in slit width while increasing usable throughput and minimizing manual interventions. The mapping below clarifies how each technology translates to operational benefits and measurable impacts.
Key technologies and their primary benefits:
To make the gains concrete, the table that follows links each technology to typical operational improvements and example metrics.
| Technology | Benefit | Operational Impact / Example Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Automatic Tension Control | Improved roll quality | Reduces telescoping and scrap; typical waste reduction 10–30% |
| Servo Drives & Motion Control | Positioning precision | Maintains slit width accuracy within ±0.1 mm at high speed |
| PLC Control & Recipe Management | Faster changeovers | Cuts setup time by 40–70% for repeat jobs |
| Web Guiding (Edge Sensor/Camera) | Reduced edge defects | Improves slit registration and print alignment consistency |
Automatic tension control—implemented with dancers, load cells, or closed-loop feedback—stabilizes web tension across the unwind, slit, and rewind zones to prevent defects like wrinkles, telescoping, and inconsistent roll diameters. Closed-loop systems measure actual tension and adjust motor torque or braking in real time, which is critical on thin films that are sensitive to over-tensioning and on labels that require strict registration. Properly tuned tension control reduces trim waste, improves slitting edge quality, and extends blade life by minimizing vibration and chatter. Troubleshooting common tension issues involves verifying sensor calibration, damping settings on dancers, and ensuring that control setpoints match material specifications; addressing these points leads naturally into servo and PLC roles in overall line synchronization.
Servo motors provide responsive acceleration, deceleration, and position control that keep slitting knives, rewind shafts, and roll indexing synchronized even during rapid format changes; this precision is crucial for maintaining slit width tolerances and avoiding roll eccentricity at high speeds. PLC control systems orchestrate the machine recipe, manage I/O from sensors, and present operators with diagnostics and changeover sequences that reduce manual errors and downtime. Together, servo drives and PLCs enable features like electronic slitting positioning, auto core handling, and predictive maintenance alerts that raise throughput and uptime. Evaluating servo sizing, encoder resolution, and PLC capabilities is therefore central when specifying a high-speed slitter rewinder for modern converting lines.

High-speed slitter rewinders are central to flexible packaging, label manufacturing, thermal paper converting, lamination lines, and roll stock preparation for bag-making and printing operations. In flexible packaging, slit rolls feed downstream bag machines or pouch formers where edge quality and slit width accuracy influence seal integrity and print registration. For label converters, narrow-web slitters maintain tight width tolerances and surface cleanliness to ensure consistent print and die-cutting. Thermal paper and receipt roll producers require high concentricity and controlled roll hardness to avoid jamming in printers. The following short examples connect typical applications to machine features and expected KPIs.
For flexible packaging lines, slit-roll surface quality and concentricity directly affect downstream sealing performance and print alignment; ensuring these parameters reduces rework and speeds final assembly. In label converting, narrow-web repeatability and servo-driven positioning support short run changeovers with fast job recall and minimal scrap. These application maps underline why buyers match machine features—turret changeover, servo drives, web inspection—to the specific needs of each production flow.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd., also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd., illustrates how a supplier can support diverse converting needs: the company reports installed machines across many countries, a dedicated R&D team for customization, and production capabilities intended to deliver samples in around three days with bulk deliveries for standard machines within roughly 15–20 days. Its stated quality processes include 100% final inspection and targeted warranty coverage on critical components, which can reassure converters evaluating suppliers for one-stop solutions. Its vendor attributes show how manufacturing capacity and service promises align with application requirements and procurement schedules.
In flexible packaging operations, slitter rewinders receive wide laminated or blown-film parent rolls and produce multiple slit rolls sized for bag-making, pouch-forming, or lamination steps, acting as the bridge between film extrusion/lamination and downstream converting. Critical quality checks include edge cleanliness, slit width accuracy, and surface inspection for pinholes or contamination that would cause seal failures. Maintaining stable tension and consistent rewind pressure ensures rolls feed reliably into automated bag machines, reducing stoppages and scrap. Converters often specify turret slitters with automatic transfer heads and in-line inspection for high-volume film production, which leads to predictable delivery of slit reels for final converting.
In paper converting and label manufacturing, slitter rewinders produce core-wound rolls to exact diameters and slit widths required by printers and slitter die-cutters; precision in slit edge quality and roll concentricity is essential to avoid misfeeds and print registration errors. Narrow-web slitting for label stock prioritizes tight slit tolerances and clean edges to ensure adhesive application and die-cutting accuracy. For thermal paper, the rewind hardness and diameter control influence dispenser performance in point-of-sale printers, so these producers focus on consistent rewind torque and thermal coating preservation. Recognizing these application-specific requirements helps purchasers specify blade systems, core handling, and inspection features correctly.
High-speed slitter rewinder machines deliver measurable benefits across productivity, quality, and cost metrics by increasing throughput, reducing manual handling, and minimizing trim waste through precise control systems. Upgrading to machines with automatic tension control, servo drives, and turret or automatic roll-handling architectures typically shortens changeover times, increases effective production hours, and lowers per-unit labor costs. The EAV table below quantifies common benefit categories and example KPIs that buyers use to estimate return on investment.
Manufacturers see benefits in throughput, precision, and waste reduction that directly translate into lower unit costs and improved delivery performance.
| Benefit | How Measured | Example KPI or Typical Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput increase | Output meters/hour or finished rolls/day | +20–40% effective throughput with turret/auto changeover |
| Precision cutting | Slit width tolerance and repeatability | ±0.1 mm slit accuracy with servo positioning |
| Waste reduction | Trim and reject rate | Trim reduction 10–30% with optimized tension and blade choices |
| Labor and downtime savings | Changeover minutes and operator hours | Setup time cut by 40–70% using PLC recipes and auto core loading |
Automation features like auto blade positioning, recipe-based PLC changeovers, and turret transfer heads reduce manual setup and shorten non-productive time, enabling more run time and higher daily output. Precision components—high-resolution encoders, stabilized servo control loops, and robust blade holders—maintain slit accuracy across shifts and formats, reducing downstream rework in printing or bag-making. In practice, an inline web-guided, servo-driven slitter can sustain tight tolerances at higher m/min speeds than older mechanically-driven equipment, meaning a converter can produce more sellable rolls per shift. These productivity and precision gains are often the decisive factors when justifying capital expenditure.
Accurate tension control and optimized slitting reduce trim losses and scrap by minimizing over-slit margins and decreasing defective roll counts; energy-efficient components and automated handling lower per-roll energy and labor inputs. By modeling scrap as a percentage of input material and applying expected reductions from improved control systems, buyers can estimate annual savings and payback periods. For example, trimming waste reduced from 5% to 3% on high-volume film lines translates directly into raw material savings and lower disposal costs. These operational efficiencies compound when combined with faster changeovers, resulting in better utilization of both machinery and labor.

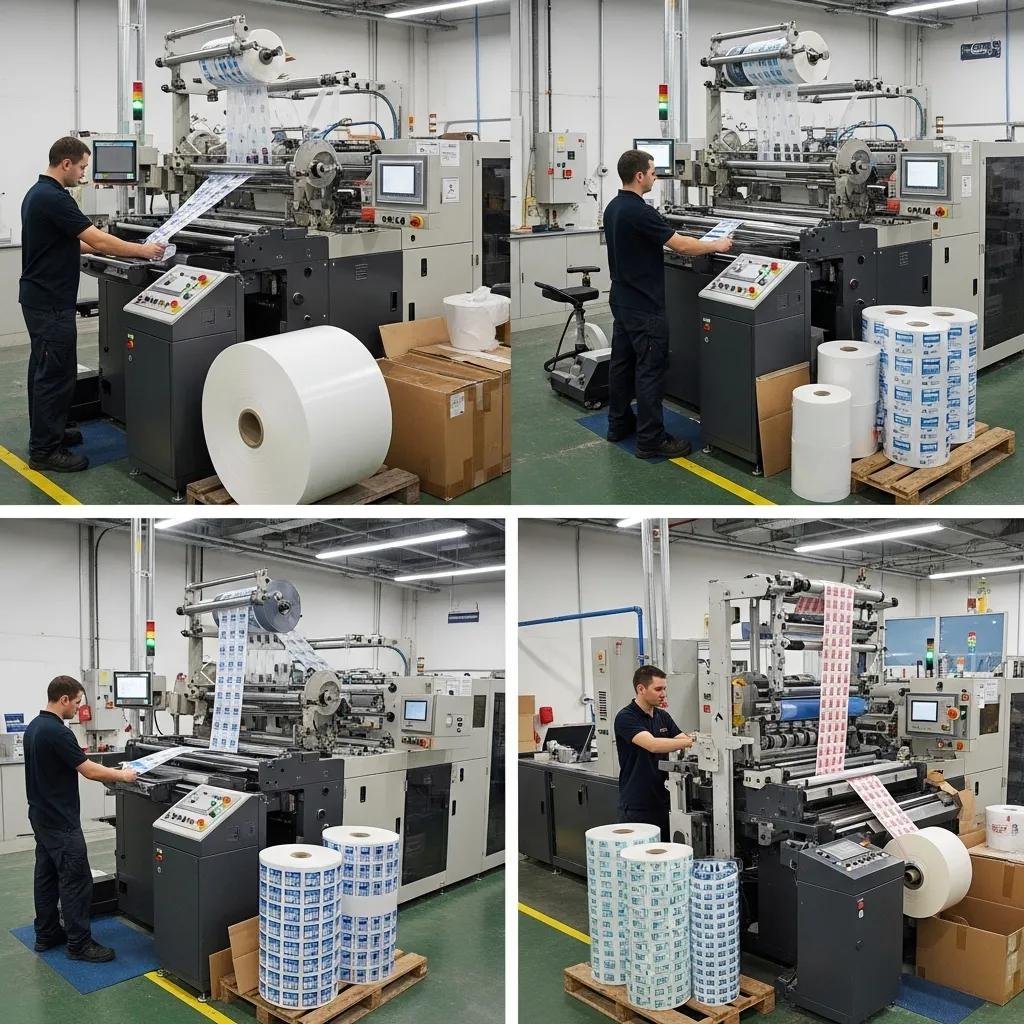
Selecting the right slitter rewinder requires a checklist-based evaluation of material types, required line speeds, slit width tolerances, rewind diameters, automation level, and supplier support capabilities. A practical buyer’s checklist helps convertors rank priorities and narrow options systematically before issuing RFQs. The checklist below presents the critical decision factors to consider during specification and vendor evaluation.
Key selection criteria checklist:
Use this checklist to prepare a minimum-spec sheet that aligns with production targets, then proceed to vendor evaluation focusing on service, warranties, and delivery performance.
When evaluating vendors, buyers often weigh warranty terms, quality assurance practices, R&D support, and delivery timelines. Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd., also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd., provides several vendor attributes that exemplify what to request in an RFQ: stated 100% final inspection to ensure product readiness, a two-year warranty on timer switches, customization options supported by an R&D team, and production capacity claims intended to enable fast sample delivery in about three days and standard bulk delivery in roughly 15–20 days. Including these specific vendor commitments in procurement conversations helps converters compare real-world supplier responsiveness and fit-for-purpose customization.
Key factors include the material family and thickness, desired line speed, minimum and maximum slit widths, target rewind diameters, required level of automation, spare-parts logistics, and total cost of ownership that factors in energy, maintenance, and labor. Technical details to specify in an RFQ are the servo encoder resolution, tension control philosophy (dancer vs. load cell), maximum unwind roll weight, and availability of in-line inspection or web-cleaning modules. Service expectations—such as operator training, spare kits, and on-site commissioning—should be written into vendor proposals to reduce ambiguity. Clear specification of these factors streamlines supplier comparisons and reduces post-installation surprises.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) positions itself as a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and bag production equipment with a one-stop service and customization capability. The company highlights several tangible strengths that buyers commonly seek: a large installed base across many countries, an R&D team for tailored solutions, 100% final inspection as part of quality checks, and warranty coverage on select components such as timer switches. In addition, the supplier references production scale with 16 production lines and claims competitive pricing due to large-scale manufacturing and skilled labor. For procuring teams, these attributes—customization support, inspection practices, and stated delivery timing—can serve as reference points when comparing proposals and negotiating lead times.
For converters ready to evaluate vendors, requesting a detailed quote that references these specific assurances—final inspection scope, warranty terms, customization timeline, and sample/bulk delivery estimates—helps convert qualitative claims into contractual commitments and reduces procurement risk. This pragmatic approach completes the buyer’s checklist and readies teams to move from specification to procurement.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;