Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

This guide defines the most common thermoplastics—HDPE, LDPE, PP, and PET—and explains how industrial recycling equipment converts waste into reusable pellets that feed circular-economy supply chains. Readers will learn material properties that determine shredding, washing, and extrusion choices, a step-by-step industrial recycling workflow, and specific machine classes that improve pellet quality and throughput. Industrial plastic recycling machines such as industrial plastic shredders, plastic washing lines, pelletizing extrusion lines, and specialized film lines matter because equipment choice affects energy use, contamination tolerance, and final rPET or PE pellet performance. The article maps each recycling stage (collection, sorting, washing, shredding, extrusion, pelletizing), drills into polymer-specific best practices for HDPE, LDPE film, PP, and PET, and highlights machine attributes that reduce waste and energy intensity. Throughout, practical lists, comparison tables, and vendor-aligned solution notes support buyers evaluating LDPE recycling machines, HDPE recycling equipment, PP recycling lines, and PET recycling machines.
HDPE, LDPE, PP, and PET are distinct thermoplastic polymers whose density, stiffness, and melting behavior determine recyclability and processing choices. HDPE (high-density polyethylene) is stiff and chemically resistant, LDPE (low-density polyethylene) is flexible and film-forming, PP (polypropylene) balances stiffness and toughness with a higher melting point, and PET (polyethylene terephthalate) provides high barrier and clarity for bottle applications. These material properties influence shredding aggressiveness, washing techniques, melt temperature windows, and the choice between single- and twin-screw extrusion. Understanding basic polymer attributes reduces downstream contamination and helps specify equipment like an industrial plastic shredder or pelletizing extrusion line. The next sections show how those properties translate into practical recycling steps and machine choices for improved pellet quality and energy efficiency.
HDPE, LDPE, PP, and PET differ mainly by density, crystallinity, and melt temperature, which determine mechanical behavior and processing windows. HDPE is high-density, crystalline, and melts around 125–135°C, making it suitable for rigid containers and durable piping that withstand high shear during shredding. LDPE is lower density and highly flexible with a melting range around 105–115°C, which increases the risk of film wrapping and requires anti-wrap feed systems. PP has a higher melting point (around 160–170°C) and semi-crystalline structure that tolerates higher extrusion temperatures but may contain fillers that affect filtration. PET is a polyester with a melting point around 250–260°C and strong barrier properties; it requires careful drying and crystallization control to avoid hydrolysis during extrusion. These contrasts guide equipment selection from granulators to vacuum degassing extruders for consistent pellet output.
Each polymer feeds distinctive product streams that shape feedstock composition and contamination risk in recycling plants. HDPE appears in rigid containers, drums, crates, and pipes where thick walls require heavy-duty shredding and aggressive washing to remove adhesives. LDPE is dominant in films, bags, and stretch wraps, generating thin, flexible scraps prone to clumping and film-ball formation during size reduction. PP is common in rigid and flexible packaging, automotive components, and woven sacks; mixed PP streams may contain pigments and fillers that demand good melt filtration. PET is the main bottle material for beverages and packaging; bottle recycling needs label and cap removal plus precise flake drying. Recognizing these end uses helps prepare sorting and pre-processing, which limits contaminants that harm extrusion and pelletizing stages.
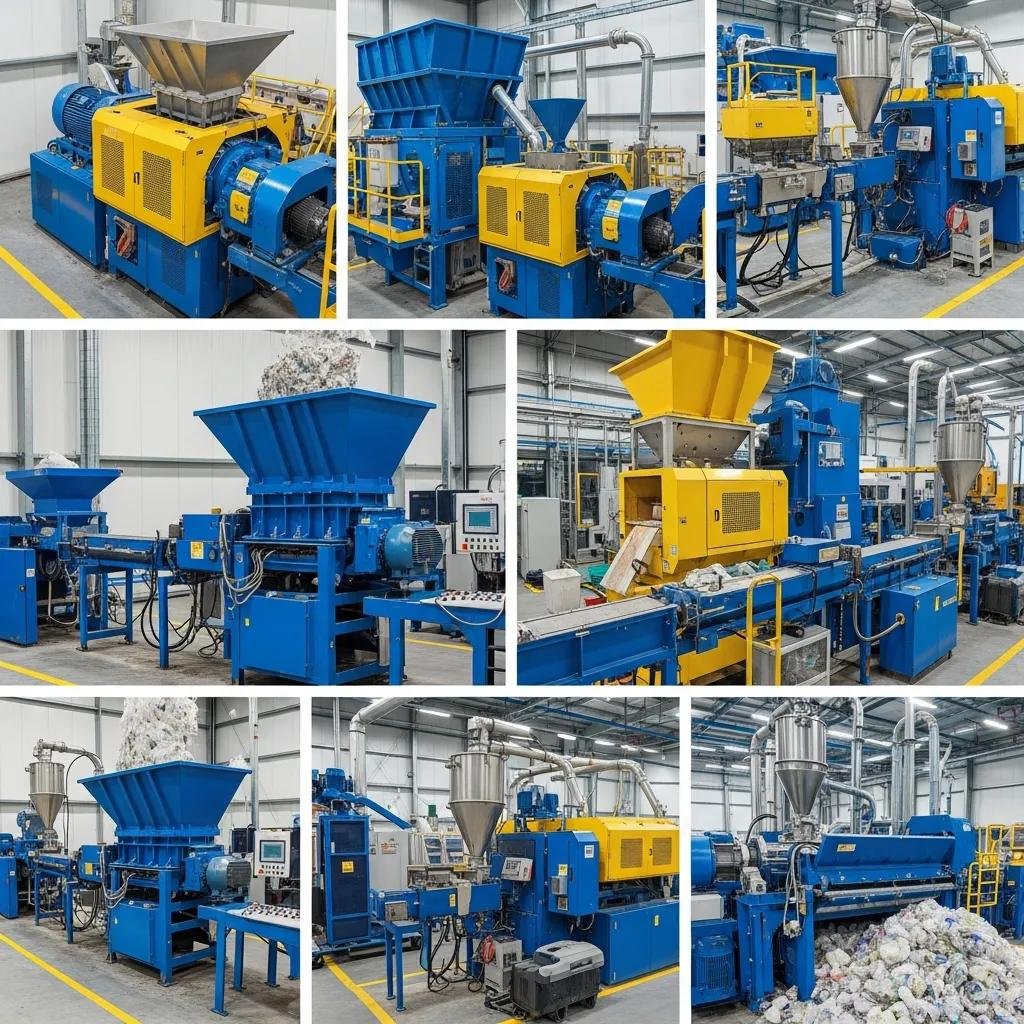
The industrial recycling workflow follows a clear sequence: collection, sorting, washing, shredding/granulating, extrusion, and pelletizing, and each step transforms feedstock to raise material purity and value. Collection concentrates post-consumer or post-industrial streams; sorting separates polymers and removes large contaminants; washing and separation remove labels, adhesives, and soils; shredding or granulating reduces size for consistent washing and melt behavior; extrusion melts, filters, and degasses contaminants; pelletizing converts melt into uniform pellets for reuse. Equipment choices—optical sorters, friction washers, industrial plastic shredders, twin-screw extruders, and water-ring pelletizers—determine throughput, energy intensity, and pellet quality. The result is material-ready pellets with controlled moisture and melt index suitable for reuse.
This process-stage table summarizes machine classes, typical outputs, and metrics used to evaluate each stage. The table clarifies where a plastic washing line matters versus where a pelletizer or granulator is the decisive investment.
| Process Stage | Machine Type | Typical Output / Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Collection & Pre-sorting | Baling & manual/automatic sort systems | Consolidated bales, contamination rate (%) |
| Optical Sorting | Optical sorter (NIR) | Polymer purity (%), throughput t/h |
| Washing & Separation | Friction washer, float-sink tanks | Clean flakes, remaining contaminants (ppm) |
| Size Reduction | Industrial plastic shredder / granulator | Particle size (mm), throughput kg/h |
| Extrusion & Filtration | Twin-screw extruder, melt filter | Melt flow index consistency, degassing efficiency |
| Pelletizing | Water-ring or strand pelletizer | Pellet uniformity, moisture content (%) |
Collection gathers mixed and sorted waste into bales or loose streams ready for processing and is the first control point for contamination reduction. Effective collection reduces downstream washing loads and increases overall yield by keeping incompatible materials separate; the output is typically bale weight and initial contamination metrics. Sorting—manual or optical—raises polymer purity using near-infrared (NIR) or density-based separation and produces homogenous streams for washing. Washing removes organics and inks using friction and chemical-assisted stages, yielding clean flakes with low suspended solids. Shredding/granulating reduces pieces to target particle sizes for uniform melting, while extrusion and pelletizing finalize melt filtration, degassing, and sizing into saleable recycled pellets. The result is material-ready pellets with controlled moisture and melt index suitable for reuse.
Machine selection depends on feedstock, throughput, and contamination tolerance: robust industrial plastic shredders and granulators reduce size; optical sorters and density separators improve polymer purity; friction washers, float-sink tanks, and dryers remove contaminants; twin-screw extruders with melt filtration and degassing prepare melt for pelletizing; pelletizing extrusion lines produce uniform pellets. When mapping solutions to stages, consider throughput (kg/h), energy consumption (kW/ton), and final pellet quality metrics (MFI, moisture). Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) supplies plastic recycling machines and complete recycling lines for PE, PP, and PET that can be specified to match expected throughput and contamination profiles; their offerings are positioned as one-stop solutions with customization, quality assurance, and warranties to reduce procurement complexity. Buyers should request performance data, energy-use estimates, and inspection protocols when comparing vendors to ensure equipment aligns with process targets and circular-economy goals.
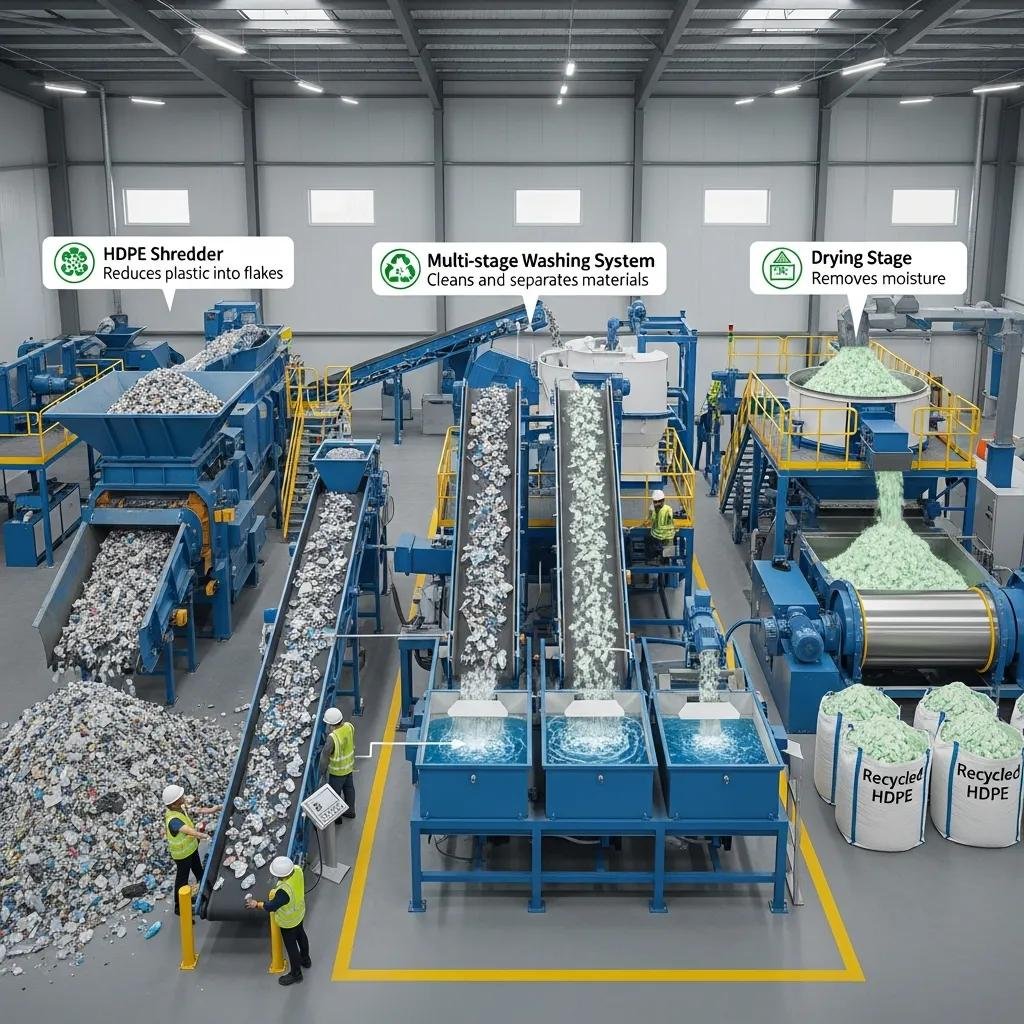

Recycling HDPE focuses on handling thick-walled rigid parts with high-density material that tolerates aggressive size reduction but needs thorough washing to remove labels and residues. Optimal HDPE recycling begins with heavy-duty shredding to reduce large containers into manageable fragments, followed by multi-stage washing including friction and float-sink separation to pull out adhesives and organic soils. Extrusion uses screw designs that control shear and temperature to avoid thermal degradation while melt filtration and degassing reduce volatile impurities. Finally, pelletizing converts clean melt into durable pellets suited for blow-molding or injection applications. These machine choices enhance pellet mechanical properties and marketability by preserving molecular weight and minimizing contamination.
For HDPE rigid feedstock, industrial plastic shredders with robust rotor/stator geometry and large feed throats are typical, delivering high throughput and the ability to process thick-walled parts without frequent jams. Granulators with heavy blades and adjustable screens produce consistent particle sizes that improve washing and extrusion feed stability; features such as anti-wrap rotors, hydraulic feed rolls, and interchangeable screens increase uptime. Selection criteria include throughput in kg/h, blade configuration for tough plastics, and residue handling to separate metal and non-plastic contaminants. After size reduction, effective dust extraction and magnetic separators protect downstream extruders and maintain pellet quality, bridging shredding performance to the washing stage described next.
Multi-stage washing for HDPE typically combines pre-wash, friction washing, and float-sink separation to remove soils, inks, and high-density contaminants, producing flakes with lower ash and moisture content. Proper drying—centrifugal or thermal—reduces hydrolysis risk during extrusion, while twin-screw extruders with controlled melt zones and filtration systems preserve polymer integrity and control melt flow index. Pelletizer choice (strand or water-ring) affects pellet geometry and cooling efficiency, impacting downstream processing. Monitoring melt temperature, shear, and filtration efficiency ensures pellets meet target mechanical properties; these process controls translate to higher-value HDPE recycling outputs and improved acceptance by end-use manufacturers.
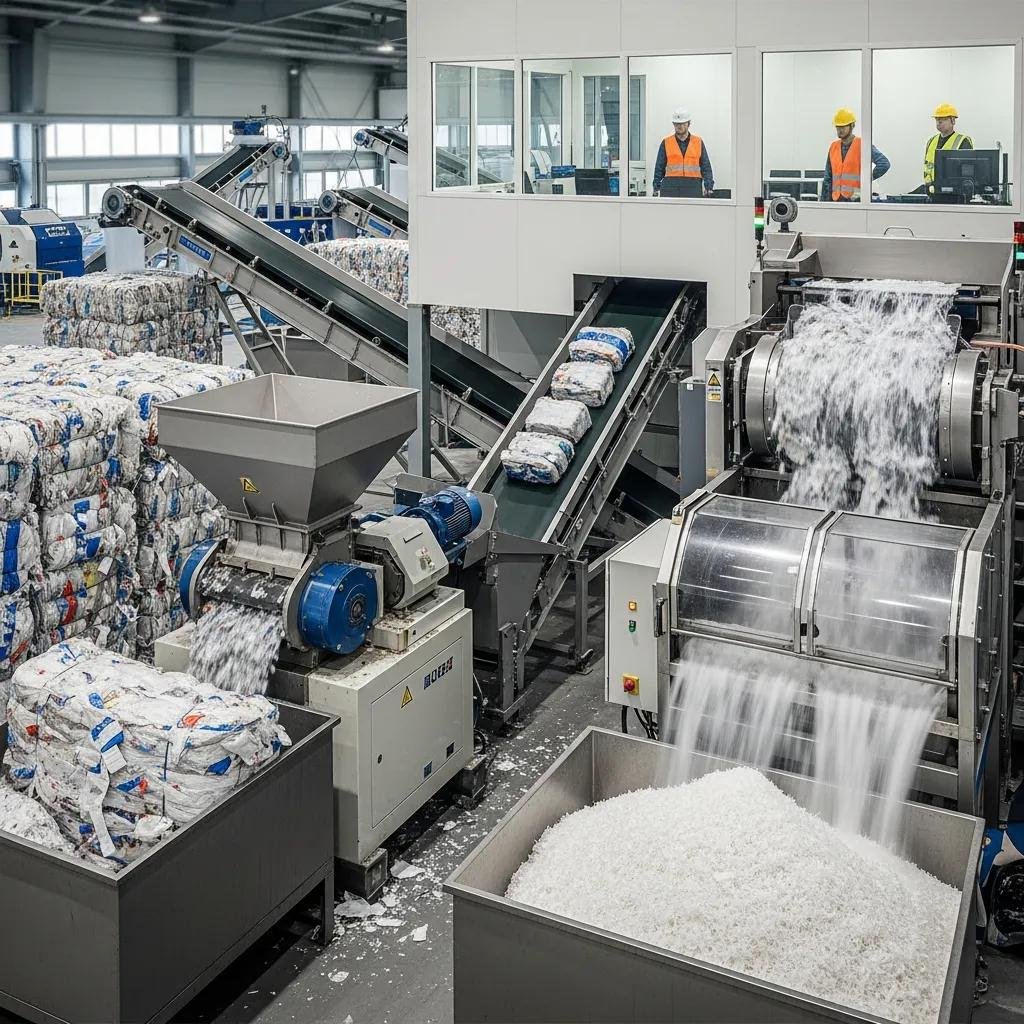

LDPE film recycling must address thinness, contamination, and film wrapping that can clog equipment and reduce throughput; best practices minimize film-ball formation and maximize wash efficiency. Pre-processing often includes de-baling, separation of heavier contaminants, and pre-shredding with anti-wrap systems. Film-specific granulators and low-speed, high-torque shredders reduce clumping; friction washers and float-sink systems remove inks and labels, while continuous dryers handle moisture-sensitive film flakes. Energy efficiency is improved through optimized screw profiles in extrusion, heat recovery in drying, and motors sized to load characteristics. The next table compares typical LDPE film recycling machine types and their key attributes to help buyers match feedstock and throughput to the right line.
| Machine Model/Type | Key Attributes (throughput, energy use, contamination tolerance) | Best-use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Low-speed rotary shredder | Medium throughput, lower kW/ton, high anti-wrap performance | Heavily contaminated films prone to wrapping |
| Friction washer line | Variable throughput, moderate energy, high removal of inks/adhesives | Post-consumer films and printed bags |
| Film flotation separator | High throughput, low incremental energy, selective density separation | Mixed polymer film streams with density contrasts |
| Continuous dryer with heat recovery | Scalable throughput, reduced net energy via heat recovery | High-moisture film flakes before extrusion |
LDPE film lines begin with de-baling and staged pre-sorting to remove bulky contamination and segregate polymer types, followed by anti-wrap shredding that reduces film to flakes without forming film-balls. Float-sink separation and friction washing remove inks and residues; surfactant use and shear rates are tuned to maximize removal while limiting polymer loss. Drying units—centrifugal or thermal with heat recovery—bring moisture below target levels before extrusion, which uses suitable screw profiles to handle low-viscosity LDPE melt. Effective process control and anti-wrap feed mechanisms prevent downtime and feed downstream extruders with consistent material for pelletizing.
Energy-efficient LDPE film recycling equipment incorporates efficient motors, optimized screw geometry, and heat recovery systems in drying and washing stages to reduce kW per ton processed. Design features such as variable-frequency drives, low-speed anti-wrap shredders, and counter-current washing minimize energy while maintaining cleaning performance. Operational best practices—thorough pre-cleaning, load balancing across lines, and scheduled maintenance—further cut energy intensity and increase uptime. When comparing suppliers, request specific energy-use data (kW/ton) and descriptions of heat recovery or motor efficiency to quantify expected operational savings and environmental benefits.
PP recycling must manage variable melting points, pigments, and filler materials while maintaining pellet stability and performance for downstream uses. Effective PP recycling uses robust shredders for size reduction, followed by wash systems tuned to remove organic soils and labels. Extrusion often benefits from twin-screw designs with degassing ports and melt filtration to extract volatiles and contaminants, while proper screw configuration controls shear and thermal exposure. Pelletizing converts filtered melt into consistent pellets, with water-ring or strand pelletizers used based on downstream drying and handling preferences. Quality control focuses on melt flow index uniformity, residual moisture, and residual non-plastic content.
PP streams—rigid containers, films, or mixed PP—require flexible size-reduction strategies: heavy-duty shredders for thick parts, mid-speed granulators for moderate-sized flakes, and adjustable screens to control particle size for efficient extrusion. Blade geometry and screen selection determine particle distribution and dust generation, which influence filtration demand. Dust and fines control through extraction and cyclones reduces contamination in melt and improves extruder longevity. Balancing throughput (kg/h) with particle-size targets ensures consistent feeding to downstream extrusion and avoids excessive backpressure in melt filtration systems.
Twin-screw extruders with degassing sections and fine melt filters remove volatiles and particulates from PP melt, stabilizing polymer chains and delivering consistent melt flow index. Melt temperature zones and screw compression ratios are chosen to limit thermo-oxidative degradation while enabling sufficient melt homogenization. Filtration systems—screen changers or automatic melt filters—capture contaminants that cause defects in final pellets. Pelletizer selection (strand vs water-ring) affects pellet cooling and surface quality; pairing the pelletizer with appropriate dryers and conveyors results in pellets that meet mechanical property and moisture specifications for reuse in injection molding or extrusion.
PET bottle recycling relies on a multi-stage approach: bottle sorting and label/cap separation, shredding to flakes, intensive flake washing, drying and crystallization, and extrusion or solid-state polycondensation for rPET production. Key equipment includes bottle washers, shredders sized for PET, hot-wash friction lines, paddle dryers, and extruders with vacuum degassing and melt filters. Innovations such as improved flake washing chemistry, in-line crystallization, and advanced melt filtration increase rPET clarity and intrinsic viscosity recovery. The table below links machine components to performance attributes and resulting rPET output quality metrics to guide line design and supplier comparisons.
| Machine Component | Attribute Tested (cleaning efficiency, flake quality, drying time) | rPET Output Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Bottle pre-washer | Label and adhesive removal rate (%) | Lower contamination, higher clarity |
| Shredder & granulator | Flake size uniformity (mm) | Even drying, better melt homogeneity |
| Hot friction washer | Ink and residual organics removal | Reduced discoloration, improved IV |
| Vacuum degassing extruder | Volatile removal efficiency | Higher intrinsic viscosity, fewer defects |
| Paddle or centrifugal dryer | Residual moisture (%) and drying time | Reduced hydrolysis during extrusion |
PET bottle lines use bottle crushers and rotary feeders to reduce bottles, then pass fragments through de-labeling and cap-removal stages to avoid hydrophobic contaminants. Shredders break bottles into flakes sized for effective wash-line contact; subsequent hot-friction washers, caustic stages, and float-sink tanks remove inks, adhesives, and PVC contaminants. Efficient flake drying—centrifugal or thermal—lowers moisture to avoid hydrolysis in melt. Shredder specs for PET emphasize blade hardness, rotor speed, and screen aperture to produce consistent flakes that maximize wash efficiency and downstream extruder performance.
State-of-the-art PET extrusion combines vacuum degassing, advanced melt filtration, and controlled crystallization to preserve intrinsic viscosity and minimize discoloration during melt processing. Chemical recycling adjuncts and depolymerization technologies can complement mechanical lines for highly contaminated or difficult-to-process streams, improving yield and polymer quality for demanding applications. Innovations such as continuous SSP (solid-state polycondensation) modules and in-line IV monitoring enable rPET production with properties approaching virgin resin. These advances make rPET more widely acceptable in high-value packaging, and they create pathways to integrate mechanical and chemical approaches for closed-loop recycling.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) offers plastic recycling machines and complete recycling lines for PE, PP, and PET aimed at delivering energy-conscious designs and customizable lines. Their positioning as a comprehensive machinery provider with quality assurance, two-year warranty on critical components, customization, and one-stop service supports procurement teams seeking predictable delivery, performance metrics, and lower defective rates. For buyers seeking detailed specifications, equipment performance data, or tailored proposals, a direct inquiry to their sales engineering teams can initiate machine selection and quoting.
For project-ready inquiries and equipment discussions, Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. can provide machine performance details, customization options, and lead-time estimates to support pilot testing or full-line procurement.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;
film blown machine, blown film extrusion, plastic bag making machine
At Kingdom Machinery Co., Ltd., we specialize in providing high-quality machinery tailored for the plastic bag and blown film manufacturing industries. Our commitment to excellence ensures that our clients receive reliable and efficient equipment that meets their specific production needs.
With years of experience in the industry, we understand the challenges faced by manufacturers. That's why we offer a range of machines designed to enhance productivity while maintaining top-notch quality. From automatic T-shirt bag making machines to advanced blown film machines, our products are engineered to deliver superior performance and durability.
Our commitment to innovation sets us apart in the plastic machinery industry. We continuously invest in research and development to integrate the latest technology into our machines, ensuring they operate at peak efficiency and produce high-quality products.
For instance, our advanced film blowing machines utilize cutting-edge technology to optimize the extrusion process, resulting in consistent film thickness and excellent tensile strength. This not only enhances the quality of the finished product but also reduces material waste, making our machines an eco-friendly choice for manufacturers.
At Kingdom Machinery, we prioritize our customers' needs and satisfaction. Our dedicated support team is available to assist clients throughout the entire process, from selecting the right machinery to providing after-sales service and maintenance.
We believe that strong customer relationships are built on trust and reliability. That's why we offer flexible customization options for our machines, ensuring they fit seamlessly into our clients' production lines. Our timely after-sales service further reinforces our commitment to providing exceptional support.
As a leading manufacturer of plastic bag machinery, we recognize the importance of environmental sustainability. Our machines are designed to minimize energy consumption and reduce waste, aligning with global efforts to promote eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
We also offer a range of recycling machines that facilitate the processing of plastic waste into reusable materials, helping businesses contribute to a circular economy. By choosing our machinery, clients not only improve their production efficiency but also play a vital role in protecting the environment.