Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.
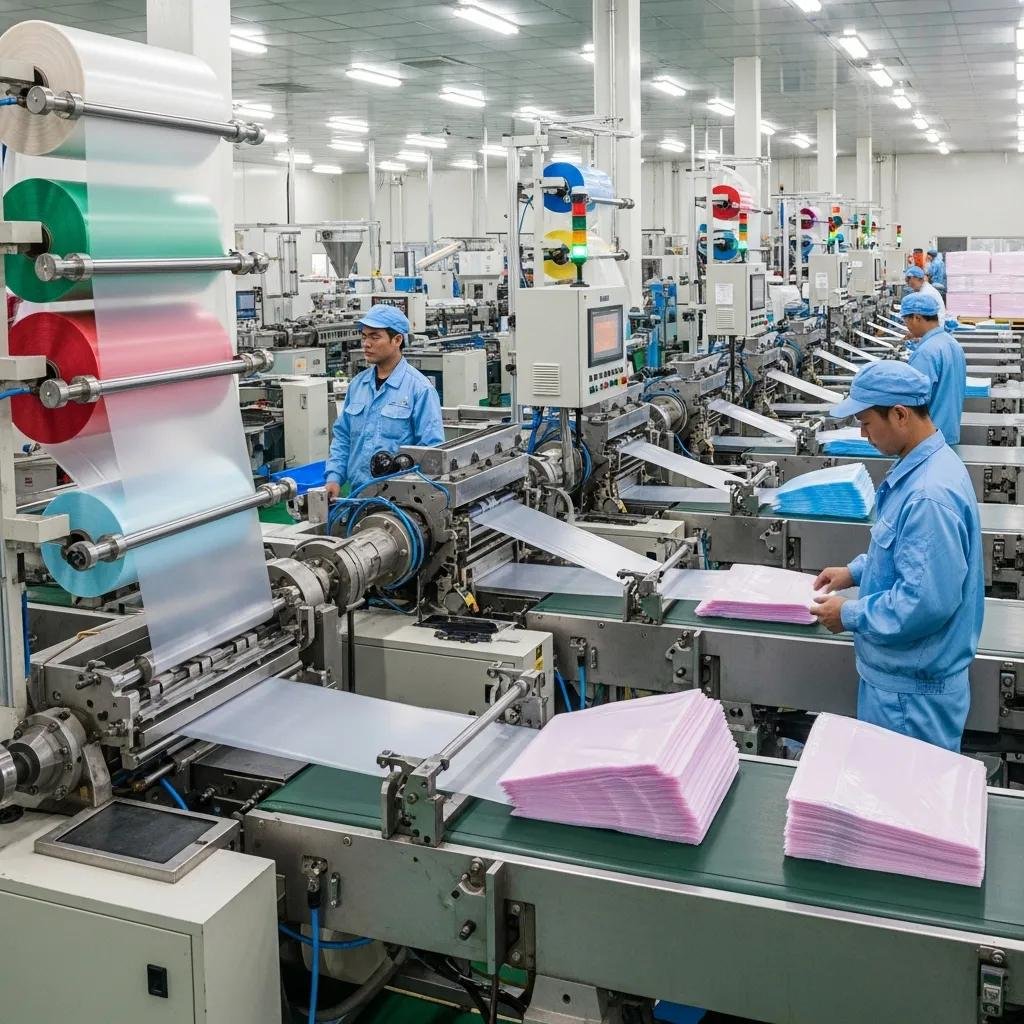

This guide defines a complete pathway to plan and launch a plastic bag production plant, explaining market identification, business planning, site selection, machinery choices, raw-material sourcing, and production quality systems. Reading this guide will help you reduce time-to-production, lower total cost of ownership, and design an efficient manufacturing flow that matches your niche—whether t-shirt bags, gusseted industrial sacks, or biodegradable shopping bags. Many startups and growing converters struggle to link market demand with the right film extrusion technology and conversion equipment; this article provides actionable steps and selection criteria to close that gap. You will find market-research steps, business-plan line items, location and layout checklists, machinery comparisons, resin tradeoffs, and process-level quality controls—all organized to support clear investment decisions. The following sections walk from identifying a niche through machine selection and supplier management to process controls and traceability, integrating practical tables and checklists to help you plan capacity, costs, and compliance.
Market research for a plastic bag factory setup begins by defining demand drivers, customer segments, and regulatory constraints that affect product choice and margins. Research combines quantitative data—volume forecasts and price bands—with qualitative insights like brand customization needs and sustainability preferences, which shape whether you prioritize conventional LDPE/LLDPE lines or biodegradable blends. The objective is to translate market signals into machine capacity, layer structure (single vs. multi-layer film extrusion), and finishing options such as printing or gusseting. A clear market definition reduces capital risk and guides downstream decisions on layout and vertical integration. The next subsection lists current industry trends that should directly influence niche selection.

Current trends show rising demand for sustainability, higher automation, and regional shifts driven by regulation and retail procurement standards, which directly influence product mix and equipment selection. Sustainability trends push converters to consider biodegradable blends and in-plant recycling to reduce resin costs and meet buyer requirements, while automation trends raise the bar for consistent gauge control and inline printing quality. Regional regulatory drivers—single-use bans or compostability labeling—will determine whether your plant needs certification-ready processes or simply cost-competitive PE production. These drivers mean that early market research must score regulatory risk and sustainability premium potential, which then informs material and machine choices. Understanding these trends sets the stage for defining a target market and the bag styles to produce.
Defining your target market requires segmenting by end-use (retail, food service, industrial), order volume, price sensitivity, and customization needs, then mapping those segments to bag types such as t-shirt bags, flat bags, or heavy-duty garbage bags. Use decision criteria that include minimum order quantity, print complexity, required barrier properties, and expected gross margin to select a specialization that matches your investment level. For example, high-volume retail suppliers may prioritize low-cost single-layer HDPE t-shirt bags, whereas branded retailers demand multi-layer blown film with flexo printing and strict gauge tolerances.
Market segmentation checklist for niche selection:
This checklist narrows feasible niches quickly and leads into planning core capital and operating requirements.
A plastic bag manufacturing business plan combines market analysis, operational design, capital and operating cost estimates, and compliance planning to demonstrate feasibility and attract funding. The plan should define the product portfolio, required production capacity, equipment list, factory layout, staffing plan, and a financial model with projected revenue, gross margin, and cash flow for at least three years. Investors and lenders expect clear capex/opex breakdowns, break-even calculations, and risk mitigation for supply volatility—especially when biodegradable resins are considered. Operational planning must also cover quality control protocols, maintenance schedules, and supply chain arrangements that ensure uninterrupted resin feeds. The next subsection provides sample financial line items and funding options to craft realistic projections.
Financial projections should itemize one-time setup costs and recurring operational expenses, then produce a break-even and payback analysis to show investor returns under conservative and optimistic scenarios. Typical funding sources include bank loans, equipment leasing, and strategic investors; each requires a clear capex schedule, cost of goods sold assumptions, and a sales ramp plan. A sample cost table below separates major cost categories and helps estimate ranges for small, medium, and larger plants to support lender dialogue and lease-vs-buy decisions.
| Cost Item | Type | Estimated Range |
|---|---|---|
| Blown film extrusion line (single/multi-layer) | One-time equipment | Moderate–High |
| Bag making & finishing machines | One-time equipment | Moderate |
| Site preparation and utilities | One-time | Low–Moderate |
| Raw material (resin) inventory | Recurring working capital | Moderate |
| Labor and supervision | Recurring Opex | Moderate |
| Utilities (electric/steam/compressed air) | Recurring Opex | Low–Moderate |
This breakdown clarifies capital needs and recurring cash requirements and supports negotiation with banks or lessors. After clarifying costs, prepare a conservative sales forecast to demonstrate break-even timing and required working capital.
Legal and regulatory requirements include business licensing, environmental permits for emissions and wastewater (where applicable), occupational safety compliance, and product labeling rules—especially for biodegradable or compostable claims. Product compliance may require certification or testing to substantiate compostability claims; therefore, labeling must reflect verified standards to avoid penalties or buyer disputes. Waste management and recycling obligations often require a plan for film offcuts and regrind handling, plus documentation and traceability if using recycled content in finished bags. Finally, local zoning and permitting will dictate allowable production hours and waste handling systems. Addressing these requirements early reduces permitting delays and aligns plant design with compliance needs.
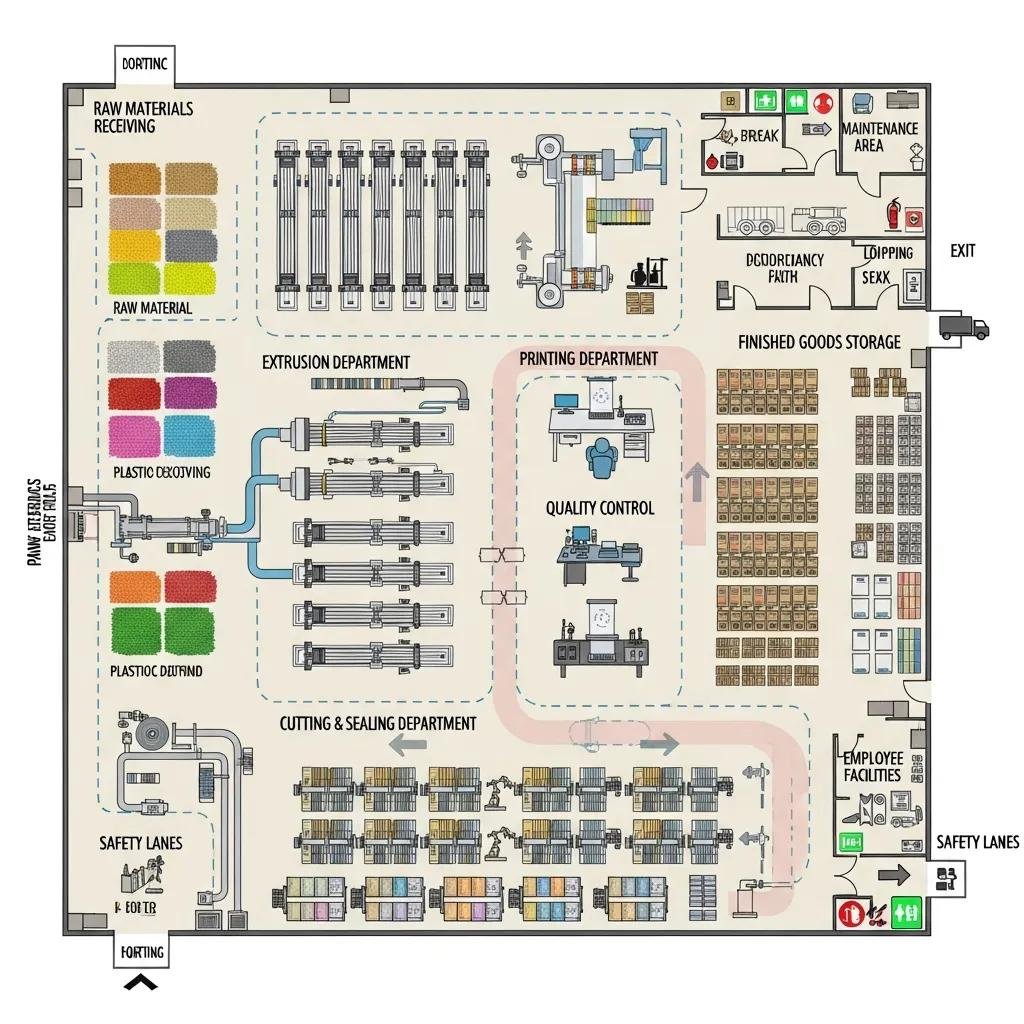
Selecting a site and designing a factory layout for a bag production line hinge on logistics, utilities, workforce availability, and the intended production flow from resin receiving to finished goods storage. Site selection must prioritize transport links for inbound resin and outbound bags, sufficient electrical capacity for extrusion ovens and air handling, and zoning that permits manufacturing and recycling operations. Layout principles favor linear flows that minimize material handling—resin silos located near extruder feeds, film winding and conversion stations sequenced to reduce intermediate storage, and space reserved for future automation or additional lines. A properly designed layout also includes maintenance access, material staging, and safety routing for forklifts. The following subsection lists site selection criteria and introduces layout optimization principles.
Site selection criteria should be scored and weighted by proximity to resin suppliers, access to transport (road/port), utility capacity (power and compressed air), labor pool quality, and local regulatory environment including incentives or restrictions. Assign weights to each criterion—such as logistics 30%, utilities 25%, labor 20%, regulatory 15%, and cost 10%—and score candidate sites to produce a weighted total that informs decision-making. Consider spare capacity for future expansion and presence of complementary industries that can supply services or materials. A transparent scoring method accelerates approval and reduces emotional decision-making in site acquisition. Next, optimize the internal layout to support this site choice with production efficiency.
Optimize layout by arranging equipment for a linear or U-shaped flow that follows resin intake → extrusion → film cooling & winder → bag making → printing/finishing → packing and storage, while leaving clear aisles and maintenance zones. Allowances for equipment footprint should include service clearances, material handling paths, and dedicated areas for recycling and regrind processing. Reserving space for automation cells, palletizing robots, or a second extrusion line protects future scalability and reduces costly relocations. Safety and utility routing should be integrated into the layout from the start to avoid retrofits that interrupt production. These layout principles lead directly into machinery selection where capacity and footprint choices finalize the physical plan.
Selecting machinery involves matching required output rates, film characteristics, and automation level to equipment classes such as blown film extruders and bag making machines, while considering energy use, footprint, and service support. Core equipment choice depends on whether you need single-layer vs. multi-layer blown film extrusion, output throughput in kg/h, and whether inline printing or lamination will be required. Auxiliary equipment—printing presses, slitting/winding stations, and recycling pelletizers—adds capability for branding and cost reduction but increases footprint and integration complexity. Use the comparison table below to evaluate machine classes by output capacity, power draw, and typical footprint to guide procurement and layout choices.
| Machine Type | Key Attribute | Typical Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Blown film extruder | Output capacity (kg/h) | Choose single vs. multi-layer by product needs |
| Bag making machine | Output (bags/min) | Match bag style: t-shirt, gusseted, flat |
| Flexo printing unit | Color capability | In-line printing reduces handling but adds complexity |
| Recycling pelletizer | Regrind throughput | ROI via resin cost savings and waste reduction |
This table helps buyers prioritize machines that align with production targets and facility constraints, and it leads into more specific machine descriptions and selection cues.
Blown film extrusion machines create the plastic film using a die head and a haul-off unit, producing single-layer or multi-layer tubing that is collapsed, cooled, and wound for conversion; choosing multi-layer capability allows barrier or stretch properties and can improve film performance. Bag making equipment converts film into finished shapes—t-shirt bag heads, flat bag cutters and sealers, gusseting stations—and is specified by output (bags per minute), seal type, and handling for printed film. Throughput selection must match market demand: undersized machines create bottlenecks while oversized machines inflate capital and utility costs. Map bag types (t-shirt, flat, gusseted, heavy-duty) to extruder die sizes and bag making configurations to ensure the line meets target KPIs for yield and cycle time.
Auxiliary machines provide differentiation and cost control: flexo or gravure printing enables brand customization and higher ASPs, while in-plant recycling pelletizers and regrinders reduce virgin resin purchases and improve sustainability credentials. In-line printing reduces handling and speeds throughput, but requires tighter register control and more precise film gauge consistency. Recycling solutions lower long-term resin exposure and can convert production scrap into usable regrind for select bag types, improving margins and environmental performance. When integrating auxiliaries, assess their footprint, integration complexity, and maintenance needs to ensure uptime targets are preserved and automation pathways remain open.
Sourcing resins and managing supply chains requires comparing conventional polyolefins with biodegradable blends, qualifying suppliers, and setting inventory policies that balance cost and risk. Resins such as HDPE, LDPE, and LLDPE differ in melting behavior, toughness, and drawdown characteristics and therefore influence die selection and cooling strategies on the blown film line. Biodegradable polymers like PLA and PBAT need processing adjustments and can carry higher price volatility, which should be reflected in financial models and supplier contracts. Implement safety-stock and reorder-point calculations that account for lead times and storage constraints to avoid production stoppages. The next subsection presents a comparative EAV table of resin properties to guide material selection.
| Resin Type | Primary Property | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| HDPE | High stiffness, low elongation | T-shirt and heavy-duty bags |
| LDPE | High clarity, good sealability | Retail and grocery bags |
| LLDPE | High toughness, puncture resistance | Stretch and heavy-use bags |
| PLA/PBAT blends | Compostability potential | Biodegradable shopping/food bags |
Conventional resins (HDPE, LDPE, LLDPE) offer established processing windows, lower and more stable pricing, and predictable mechanical properties, while biodegradable resins like PLA and PBAT require altered extrusion temperatures, may need different die-gap and cooling settings, and often command a premium price. Processing considerations include melt index, cooling behavior for bubble stability, and sealing temperatures; biodegradable blends sometimes need additives or compatibilizers for acceptable toughness. Certification for compostability or biodegradability introduces labeling responsibilities and potential testing costs. These technical and commercial differences necessitate supplier discussions and pilot runs before full-scale adoption to avoid quality and margin surprises.
To establish reliable suppliers, perform qualification audits focusing on consistency, lead-time reliability, financial stability, and technical support for process troubleshooting; negotiate contract terms that include minimum supply guarantees or price-stabilization clauses where possible. Inventory management should calculate reorder points using average daily consumption, lead time, and safety stock; an example formula is reorder point = lead time demand + safety stock, where safety stock covers demand variability. Long-term contracts reduce spot-price exposure, while short-term spot buys can exploit price dips; choose a mix that aligns with cash flow and risk appetite. Strong supplier relationships, supported by clear quality specifications and testing protocols, reduce production interruptions and support product consistency.
The manufacturing process flows from resin receiving and drying through blown film extrusion, bubble control and cooling, winding, conversion (cutting, sealing, handle punch), printing if required, and final packing—each step includes control points for gauge, tensile properties, and seal strength. Quality assurance integrates inline gauges, tensile testers, and seal testers with statistical sampling plans to ensure product consistency across shifts. Traceability should capture resin batch, machine run data, and QC test results to support customer claims and compliance, especially when biodegradable content or recycled content is declared. The following subsection explains core extrusion, cutting, and sealing mechanics and common process parameters to monitor.
Film extrusion centers on the die head and bubble control: resin melts in the extruder, is forced through a circular die to form a tube, and air inflation creates the bubble whose diameter and frost line determine film thickness and orientation; haul-off speed and nip roll settings control the final gauge. Cutting and sealing for bag making use heat-seal bars, ultrasonic or mechanical cutters depending on resin and bag style, with seal dwell time and temperature tuned to achieve reliable seals without burn-through. Common processing ranges depend on resin melt index and extruder capability but controlling melt temperature, cooling air, and haul-off stability is essential to limit gauge variation and maintain print registration. Consistent film quality here reduces downstream scrap and supports high uptime on finishing equipment.
Quality control measures include inline gauge measurement, regular tensile and elongation testing in a lab, seal-strength testing, and visual print inspection to meet customer specifications and regulatory labeling claims. Implement a sampling plan—such as a fixed sample per shift or per production batch—combined with acceptance criteria for gauge tolerance, tensile strength, and seal integrity; maintain records that link QC outcomes to resin batch numbers for traceability. Use automated inline measurement where possible to detect deviations early and trigger corrective actions, which reduces waste and protects margin. A robust QA program aligned with documented procedures both improves product reliability and simplifies conversations with buyers about specification conformance.
For factory owners seeking equipment and integration support, Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) supplies complete bag production lines including blown film extrusion machines, plastic bag making machines, flexo and gravure printing options, recycling machines, and specialized lines for t-shirt and biodegradable bag production. Kingdom Machine emphasizes service propositions such as 100% final inspection, two-year warranty coverage, a one-stop service model from innovation to mass production, flexible customization, energy-efficient machines, recycling solutions, and global delivery experience with over 1,700 installations across more than 100 countries. If you need tailored machine packages that match the niche selection and layout choices described above, request technical specifications and a quotation to align capacity, multilayer capability, and on-site support with your business plan.
Key equipment and service considerations when requesting quotes:
These procurement details ensure machine proposals map directly to production targets and quality requirements.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;