Reliable Spare Parts and Components for Your Machines
Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.
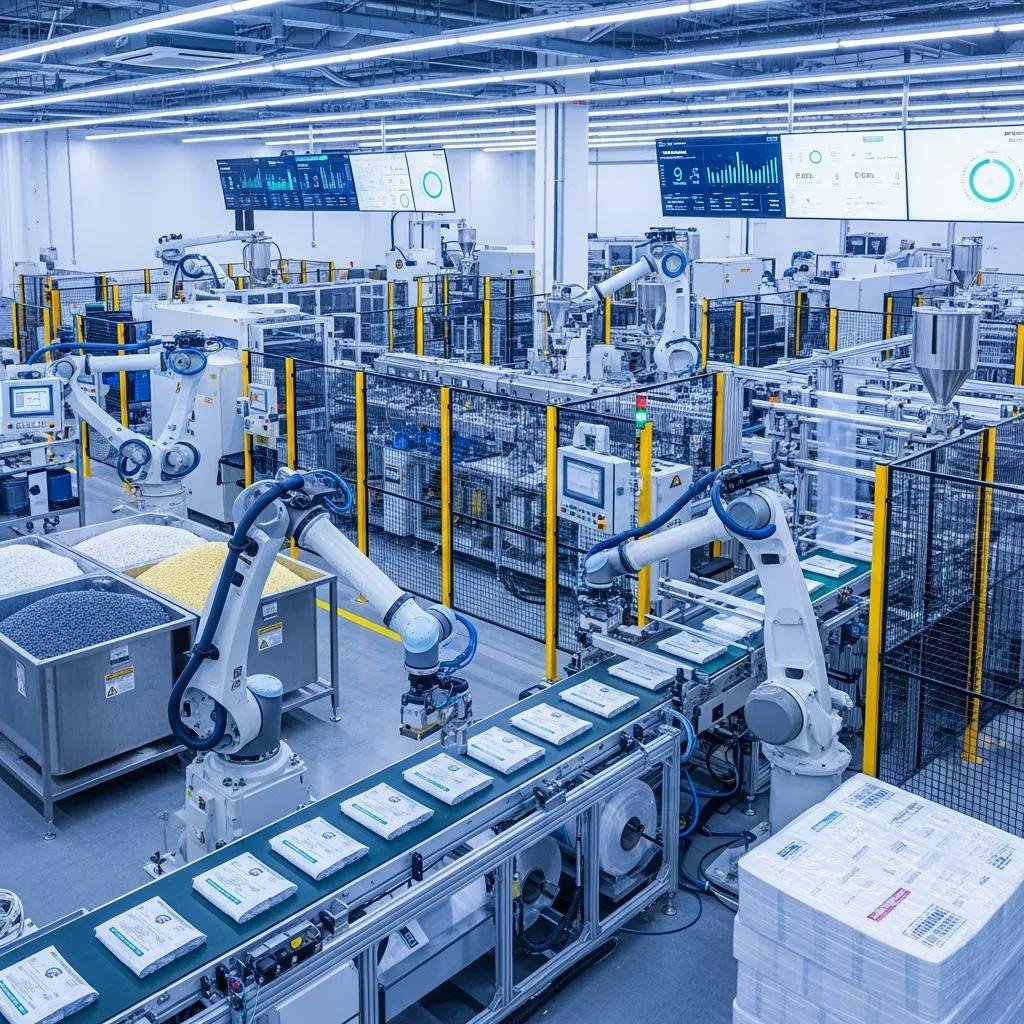

Automation in plastic manufacturing refers to the application of integrated hardware and software systems—robotics, PLCs, sensors, AI, and MES—to perform tasks that were once manual, improving throughput, quality, and sustainability. This article explains why automation matters for blown film extrusion and plastic bag production, examines the core enabling technologies, and maps practical implementation steps for modern factories. Manufacturers face pressure to increase output while reducing scrap, energy use, and labor exposure; automation provides deterministic control and data-driven optimization that directly address these pain points. Readers will learn which technologies drive results, how automated blown film and bag-making machines transform operations, the measurable benefits to expect, and stepwise guidance for deploying smart factory solutions. The piece also highlights practical examples and lessons drawn from documented supplier capabilities, helping decision-makers evaluate equipment fit and next steps for pilot projects.
Automation in plastics is powered by a constellation of core technologies that together enable closed-loop control, data-driven optimization, and hands-off operation. These technologies include industrial and collaborative robots for handling, PLCs and servo drives for precise motion control, machine vision and inline sensors for quality assurance, and higher-level systems like MES and AI for process optimization and predictive maintenance. The combination of these systems creates a cyber-physical feedback loop where sensor data informs control logic and analytical models, reducing variance and improving first-pass yield. Understanding these building blocks lets manufacturers choose targeted upgrades that yield the best ROI for specific production lines.
Robotics play specialized roles across extrusion and finishing stations, which we explore next to show task-level benefits and integration points that tie into PLC and MES layers.
Robotics and automation work hand-in-hand with AI and IoT to deliver continuous monitoring and adaptive control, which leads into a closer look at robotics on extrusion and bag-making lines.
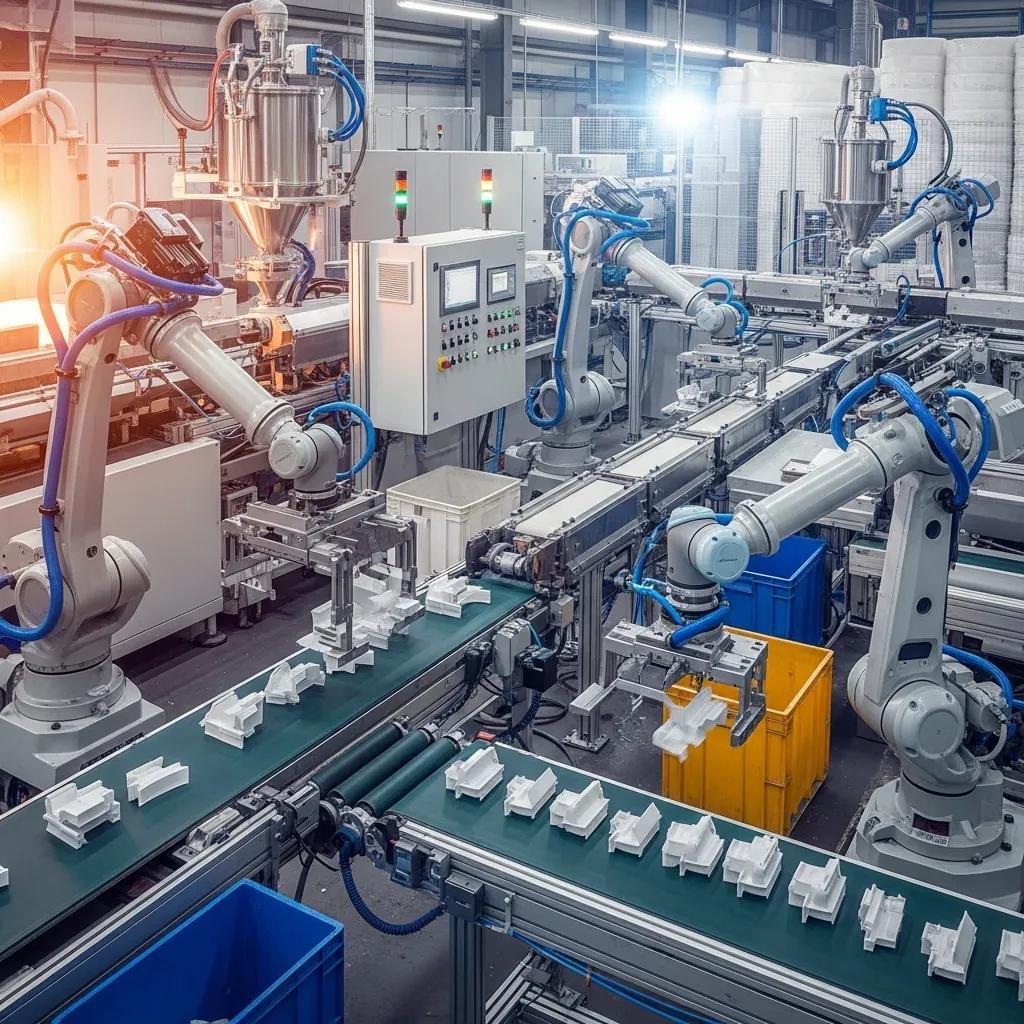

Robotics in extrusion and bag making perform material handling, machine tending, cutting, stacking, palletizing, and quality sorting, reducing manual touchpoints that cause defects and injuries. Industrial robots handle heavy rolls and finished stacks while cobots perform close-proximity tasks like part inspection and feeder adjustments; both reduce labor intensity and improve repeatability. Typical integration pairs robots with vision systems and PLC signals so that pick-and-place or roll changes occur only when quality checks pass, minimizing stoppages. The predictable motion and programmability of robots also enable faster cycle times and more consistent packaging, which directly increases throughput.
Robotics implementations should start with well-defined tasks and ROI metrics such as cycle time reduction and scrap avoidance, which prepares the line for higher-level Industry 4.0 features like predictive maintenance and digital twins.
Artificial intelligence augments automation by analyzing production data to detect anomalies, optimize extrusion parameters, and predict equipment failures before they occur, thereby improving uptime and reducing scrap. Machine learning models trained on sensor streams and vision-derived defect labels can classify defects in real time and recommend corrective parameter changes to the control system, creating a closed-loop quality process. AI also supports recipe optimization for extrusion—adjusting temperature, speed, and die gap to maintain target thickness while minimizing energy use. When AI is combined with edge computing and secure data pipelines, it allows both local real-time responses and longer-term trend analysis for continuous improvement.
Integrating AI requires structured data, labeled examples, and a phased rollout—starting with anomaly detection, then moving to prescriptive control—so teams can validate models against operational KPIs before full deployment.
Automated film production machines replace manual adjustment and inspection with closed-loop controls and autonomous subsystems, raising throughput and reducing variability across runs. Key features on modern blown film lines include PLC/HMI controls, automatic thickness control, automatic roll change, edge-trim recycling, and integrated diagnostics that allow operators to supervise multiple lines from a central console. These capabilities shorten setup time, reduce scrap during grade changes, and improve operator utilization by removing repetitive tasks. As a result, factories can achieve steadier production and more consistent film quality while better supporting sustainable materials and recycling loops.
Below is a compact comparison of common automated machine classes and how their feature sets map to operational outcomes to aid decision-making.
The following EAV-style comparison helps manufacturers assess which machine class aligns with their throughput and sustainability goals.
| Machine Class | Key Features | Typical Operational Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Blown Film Extrusion Machine | PLC/HMI control, automatic thickness control, edge-trim recycling | Higher consistency and reduced manual intervention with improved scrap handling |
| Automatic T-shirt Bag Making Machine | Servo-driven feeding, automatic sealing/cutting, recipe control | Faster changeovers and stable bag dimensions enabling higher throughput |
| Stretch Film Production Line | Controlled winding, automatic roll change, web tension control | Steady roll quality for packaging applications with lower operator workload |
This comparison highlights how feature-driven automation reduces hands-on work and supports continuous production, which in turn enables higher uptime and predictable output.
Automated blown film lines combine precision control elements—servo drives, PLCs, automatic thickness gauges, and automatic roll change systems—to maintain film properties within tight tolerances. Thickness control systems use inline gauges and closed-loop feedback to adjust screw speed or die gap dynamically, which reduces off-spec material and downstream waste. Automatic roll change and splicing subsystems minimize downtime during winding, enabling near-continuous operation and more efficient labor allocation. Integrated diagnostics and HMI visualization provide real-time KPIs that help operators and engineers act quickly on trends, further stabilizing quality and energy consumption.
Choosing machines with modular automation subsystems allows staged upgrades: start with thickness control and roll change automation, then add vision and AI for incremental improvements that compound over time.
Smart bag-making machines use servo-driven feeders, PLC-controlled sealing and cutting, and recipe-based setups to deliver repeatable bag dimensions across material grades, including biodegradable resins. Recipe control stores parameters for temperature, sealing pressure, and cutter timing, enabling fast grade changeovers with minimal scrap. When combined with inline inspection and automatic waste handling, these systems reduce rejected parts and facilitate recycling of edge trim. Additionally, compatibility with biodegradable materials makes it easier for converters to run sustainable products without extensive manual re-tuning, supporting customer demand for lower environmental impact.
Adopting smart bag machines reduces operator dependency and supports product diversification, which prepares manufacturers to meet evolving sustainability requirements while preserving line efficiency.
Automation delivers measurable improvements across efficiency, quality, safety, and sustainability by substituting deterministic control for manual variability. Automated systems increase throughput through continuous operation and faster changeovers, improve first-pass yield with inline inspection and closed-loop control, reduce workplace hazards by minimizing manual handling, and enable better resource utilization via energy monitoring and process optimization. Together, these benefits reduce unit costs and support compliance with tighter product specifications. Below is a structured view of common automation features and their typical impacts, which helps translate technology choices into business outcomes.
The next paragraphs explain how these benefits materialize in day-to-day operations and what metrics to monitor to measure success.
| Automation Feature | Metric Improved | Measurable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| PLC/HMI control systems | Uptime and setup time | Faster changeovers and centralized control leading to improved availability |
| Machine vision inspection | Defect detection rate | Earlier detection and rejection of defects; supports quality targets such as defect rates held within production QC ranges (e.g., 1–3% defective control during production) |
| Automatic roll change | Downtime per roll | Reduced manual roll swaps and shorter non-productive intervals, supporting continuous runs |
This table clarifies how specific automation elements translate into operational metrics that managers can track to validate ROI.
Automation enhances efficiency by enabling continuous production, reducing manual interventions, and minimizing changeover times through recipe-driven setups and automatic material handling. By automating repetitive tasks, the effective output per operator increases and lines can run longer with fewer stoppages for manual adjustments. Measurable outcomes include increased cycles per hour, higher overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), and the ability to scale capacity without linearly increasing labor costs. Implementing automation in targeted bottleneck areas often yields the quickest productivity gains and creates capacity to absorb new product runs.
A phased approach—pilot an automated subsystem, measure gains, then scale—helps teams validate assumptions and optimize investment decisions before full line retrofits.
Automation improves quality by using inline sensors, machine vision, and closed-loop controls that detect deviations and adjust process variables instantly, reducing scrap and rework. Real-time monitoring of thickness, temperature, and web tension ensures that products remain within specification and that off-spec material is segregated or recycled immediately. KPIs such as first-pass yield, scrap rate, and customer rejection rates become easier to monitor and improve with automated alerts and trend analysis. These capabilities not only lower material costs but also support sustainability goals by minimizing raw material consumption and improving recyclability of edge trim.
Deploying inspection and closed-loop control at critical control points creates a feedback-rich environment that informs both immediate corrections and longer-term process refinements.
At the end of this benefits discussion, manufacturers exploring equipment options can consider suppliers whose product families emphasize reliability, modularity, and strong after-sales support.
For organizations ready to source machines, Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) documents a broad product portfolio including blown film machines, automatic T-shirt bag making machines, automatic plastic shopping bag making machines, and biodegradable bag making machines that align with the automation features described above. Their offerings emphasize reliable, efficient, and easy-to-maintain equipment with one-stop service and customization options, backed by QC practices that include 100% final inspection and defective-product control reported between 1% and 3% during production. Delivery timelines and manufacturing capacity—standard machines in approximately 15–20 days, customized machines in 30–60 days, and sample availability within 3 days—support predictable project planning and faster time-to-deploy for automated line upgrades.
Industry 4.0 brings digital connectivity, data analytics, edge computing, and cyber-physical systems to plastic manufacturing, enabling machines to be monitored, optimized, and coordinated across the factory floor. Digital twins, cloud-enabled analytics, and integrated MES/ERP flows convert machine-level telemetry into actionable insights for production planning and predictive maintenance. As factories adopt these concepts, machinery design shifts toward built-in connectivity, standardized data models, and secure remote diagnostics. The net effect is greater agility—faster changeovers, remote troubleshooting, and continuous performance tuning—enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands.
The next sections break down the specific Industry 4.0 components and emerging trends that will shape machine capabilities and operations in the coming years.
Industry 4.0 refers to the integration of cyber-physical systems, IoT, and analytics into manufacturing, enabling machines to self-optimize and communicate across production systems. For plastic production machinery, this means embedded sensors, standardized OPC-UA or similar data interfaces, and support for remote monitoring and predictive algorithms. The immediate impacts include reduced mean time to repair (MTTR) through guided diagnostics, more predictable maintenance windows via condition monitoring, and improved scheduling accuracy through real-time throughput data. Machines designed for Industry 4.0 also simplify scaling from pilot to full line by exposing consistent data schemas.
Adopting Industry 4.0 capabilities requires alignment between machine data outputs and factory IT systems, which sets the stage for the next topic: future trends and where investments deliver the most value.
Future trends include tighter AI integration for process optimization, wider use of digital twins for virtual commissioning and scenario testing, increased deployment of cobots for flexible tasks, and an emphasis on energy-efficient drives and heat recovery to meet sustainability objectives. Modular machine architectures that support quick reconfiguration will enable more product variability without lengthy changeovers. Additionally, edge analytics and federated learning approaches will allow models to improve across sites without sharing raw data, preserving IP and enabling collective learning. These trends converge on a future where production lines are more responsive, lower carbon, and easier to maintain.
Manufacturers should prioritize modular, connected machines and pilot AI-driven optimization projects to capture early benefits and de-risk broader rollouts.
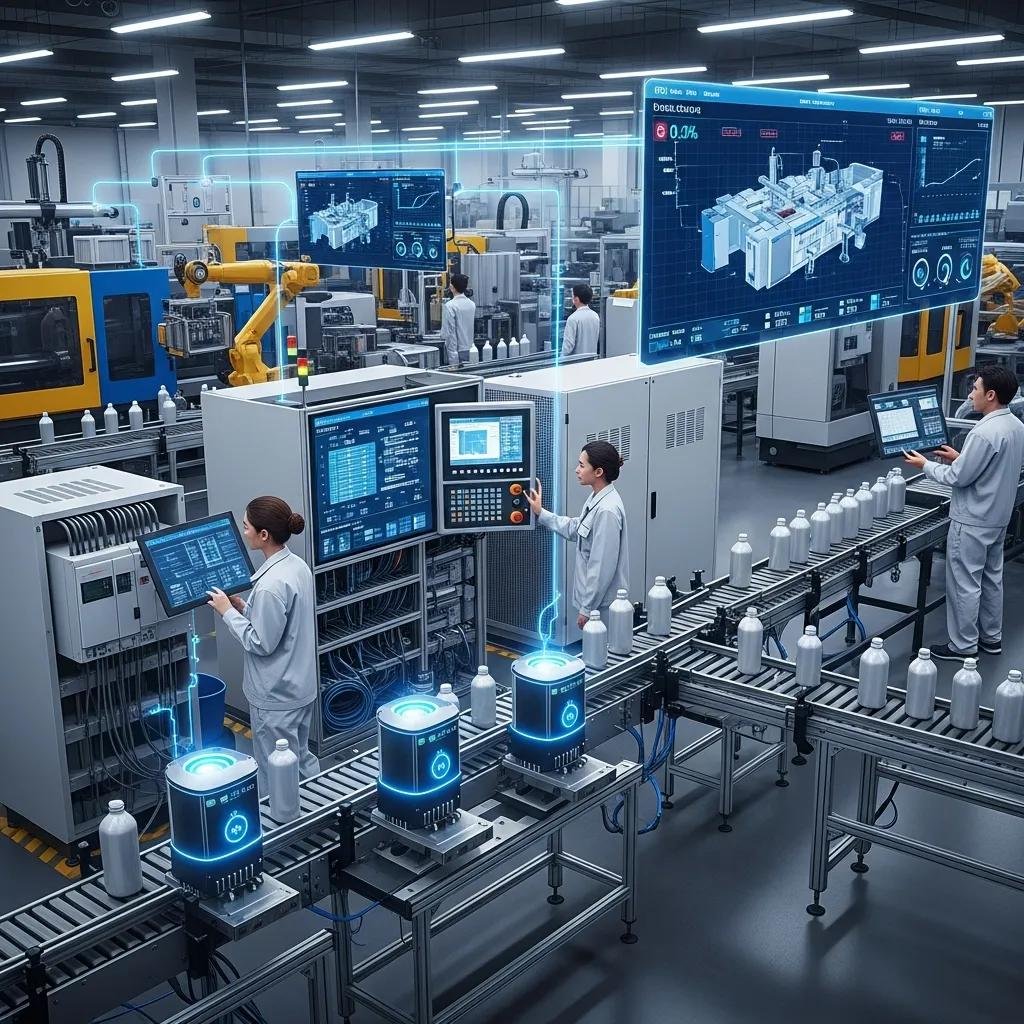

Implementing a smart factory for plastic packaging equipment follows a phased pathway: assess current capability, prioritize high-impact lines for pilots, deploy sensors and PLC/MES integration, validate improvements, and scale successful pilots across production. Core components include IoT sensors for key process variables, PLCs with modern HMI, a reliable network backbone, and MES or SCADA for orchestration and traceability. Governance—data ownership, cybersecurity, and KPI alignment—must be defined early to ensure that automation investments produce measurable business outcomes. A stepwise approach reduces risk by demonstrating value in targeted areas before committing to full-factory transformation.
Below is a practical mapping of integration components to expected outcomes to guide implementation planning.
Introductory paragraph for the EAV table that maps components to outcomes.
| Component | Integration Component | Practical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| IoT sensors | Temperature, pressure, thickness sensors at critical points | Early anomaly detection and reduced downtime through alerts |
| PLC/MES integration | Real-time control and production tracking | Centralized visibility enabling better scheduling and reduced setup time |
| Digital twin | Virtual model of line behavior and scenarios | Virtual commissioning and performance simulation that shorten ramp-up time |
This mapping shows how specific integrations translate into measurable operational improvements and provides a checklist for pilot scoping.
Integrating IoT and smart sensors enables continuous monitoring of temperature, pressure, thickness, tension, and energy use, converting analog signals into actionable data streams for control and analytics. Sensor-driven alerts reduce unplanned stoppages by flagging drift before failures occur, and energy monitoring identifies high-consumption subsystems for targeted efficiency projects. Pilots should track KPIs such as downtime reduction, energy per ton produced, and variance in thickness to quantify benefits. Proper sensor placement and calibration are essential to get reliable signals that feed both local control loops and higher-level analytics.
Starting with a focused pilot—one line or a critical machine—allows teams to validate sensor selection, data quality, and expected operational improvements before scaling.
Digital twins replicate machine and line behavior in software, enabling virtual commissioning, what-if analyses, and continuous optimization without interrupting production. When combined with predictive maintenance models driven by sensor data, digital twins can recommend maintenance actions that prevent failures, extend component life, and reduce spare-parts inventory. The workflow typically captures historical sensor patterns, labels failure modes, trains prediction models, and triggers maintenance tickets when the model predicts elevated failure risk. Metrics to evaluate pilots include reduced unplanned downtime, lower maintenance cost per unit, and increased mean time between failures.
Pilots that pair a digital twin with targeted predictive maintenance on high-impact equipment often deliver the fastest and most defensible ROI, enabling broader adoption across the plant.
Real-world automation projects typically show improvements in throughput, quality, and sustainability, whether on blown film lines or bag-making machines. Case studies commonly focus on three areas: reduced scrap through closed-loop control, faster changeovers via recipe management, and reduced labor through robotic handling and automatic roll change. While outcomes vary by line and product mix, the recurring lesson is that incremental automation—targeted at the largest pain points—delivers measurable gains that compound as systems integrate. The section below summarizes typical before/after patterns and lessons that guide replication.
The following subsection highlights ROI drivers and then extracts supplier-specific lessons that inform vendor selection and project scoping.
Automated solutions typically drive ROI through labor reduction, scrap minimization, and energy optimization, with payback profiles that depend on production volume and product complexity. Common drivers include fewer operators per shift, less off-spec material thanks to inline control, and lower energy consumption through optimized process settings. Sustainability gains arise from reduced raw material waste, more effective recycling of edge trim, and the ability to run biodegradable resins with stable quality. While exact payback periods vary, these ROI components consistently appear across industry case summaries and support business cases for phased automation investments.
Presenting these ROI drivers as part of a business case helps stakeholders prioritize projects that balance speed-to-value and strategic impact.
Kingdom Machine Co., Ltd. (also known as China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd.) provides a practical example of supplier capabilities relevant to automation projects: a diverse product portfolio that includes blown film machines, plastic bag manufacturing machines (such as Automatic T-shirt bag making machines and Automatic Plastic Shopping Bag Making Machines), flexible and gravure printing machines, stretch film machines, and recycling equipment. Their approach—100% final inspection during production, defective products controlled between 1% and 3%, R&D resources across structural, software, and circuit engineering, and a two-year warranty for timer switches—indicates an emphasis on reliability, customization, and post-sale support. Production capacity with multiple production lines and an internal lab for testing supports faster prototype-to-production cycles, which shortens time-to-deploy automated solutions.
These attributes suggest that partnering with suppliers who combine strong R&D, stringent QC, and flexible manufacturing can materially reduce deployment risk when implementing automation at scale.

Elevate your machinery performance with our premium spare parts and components. Trust in our quality and reliability for optimal operation and longevity.

Maximize efficiency with expert installation for your plastic production machines. Our professional team ensures optimal performance tailored to your needs.

Transform your concepts into reality with our tailored installation solutions. Experience professional guidance and exceptional results designed just for you.

Elevate your production with essential tips for selecting the right plastic bag making equipment. Make informed choices for efficiency and quality today.
China Evergreen Machinery Co., Ltd. is a manufacturer and supplier of plastic film and plastic bag production equipment for the entire factory, including blown film machines, bag making machines, flexible printing machines, copper tube machines, recycling extruders, stretching film machines, and foaming machines.
Whatsapp:0086-13088651008;